What is the Difference Between WordPress and WooCommerce
Optimize your WordPress online store

If you are new to WordPress and SEO and UX, and where you will see it in daily work.”>WooCommerce, it is easy to confuse them and wonder what each one actually does. WordPress and WooCommerce are related but not the same thing. WordPress is the core website platform, while WooCommerce is an ecommerce plugin that adds store features to WordPress.
In this guide, you will learn how WordPress and WooCommerce fit together, where they differ, and when you only need WordPress versus when you should add WooCommerce for online selling.
What You Need to Start
- A basic understanding of what a website is and how domains and hosting work.
- Access to a web host that supports installing WordPress.
- Administrator access to an existing WordPress site or plans to create one soon.
- A general idea of whether you want a blog, business site, or full online store.
Understanding WordPress as a Platform
WordPress is a content management system that powers your entire website. It handles pages, posts, menus, users, themes, and plugins. Think of WordPress as the operating system for your site.
With WordPress alone you can publish blog posts, add service pages, create forms, and manage your site design using themes and page builders. You can extend it with plugins for SEO, security, performance, and more.
On its own, WordPress does not know anything about products, carts, or checkout. It needs an ecommerce plugin, such as WooCommerce, to add those store features.
Understanding WooCommerce as a Plugin
WooCommerce is a plugin that installs on top of WordPress. It does not replace WordPress; it extends it. After you install WooCommerce, your WordPress site gains new features for selling products and services.
WooCommerce adds product post types, shopping cart and checkout pages, order management, customer accounts, and payment and shipping settings. It uses WordPress users, themes, and plugins underneath so everything stays in one system.
You must always have WordPress first. Without WordPress, WooCommerce cannot run by itself.
Key Differences Between WordPress and WooCommerce
Use this comparison to keep the roles of each part clear in your mind.
| Aspect | WordPress | WooCommerce |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Website platform and content management system | WordPress plugin for ecommerce |
| Main purpose | Manage content, pages, design, and users | Manage products, carts, checkout, and orders |
| Required for the other | Works alone with or without WooCommerce | Requires WordPress to work at all |
| Typical use | Blogs, portfolios, company sites, landing pages | Online stores, bookings, memberships, digital products |
| Extensibility | Themes and plugins for many features | Extensions for payments, shipping, subscriptions, and more |
From a technical perspective, WooCommerce is just code that hooks into WordPress. Developers often check whether WooCommerce is active before running store-specific logic.
if ( class_exists( 'WooCommerce' ) ) { // Run code that depends on WooCommerce. }This simple check confirms again that WooCommerce lives inside WordPress, not beside it.
When You Only Need WordPress
You do not always need WooCommerce. Many sites only require WordPress without any ecommerce features. Use WordPress alone when your site is focused on publishing content rather than processing payments.
- Personal or professional blogs that share articles and tutorials.
- Small business sites that collect leads through forms instead of selling directly.
- Portfolio or resume sites that showcase work without product listings.
- Simple brochure sites for local services where inquiries happen by phone or email.
In these situations, adding WooCommerce can create unnecessary complexity. You can still use other plugins for SEO, performance, and lead generation without turning your site into a full store.
When You Should Add WooCommerce
Add WooCommerce when your site needs true ecommerce features such as carts, payments, and order tracking. You start with WordPress, then layer WooCommerce on top.
- You want to sell physical products and ship them to customers.
- You sell digital downloads such as ebooks, courses, or templates.
- You need to accept bookings or appointments with payment at checkout.
- You plan to offer memberships or recurring subscriptions.
If you already have a WordPress site, you usually follow these high level steps to add WooCommerce:
- Sign in to your WordPress Dashboard with an administrator account.
- Navigate to Plugins » Add New.
- Search for WooCommerce, click Install Now, then click Activate.
- Follow the WooCommerce setup wizard to configure store details, payments, and shipping.
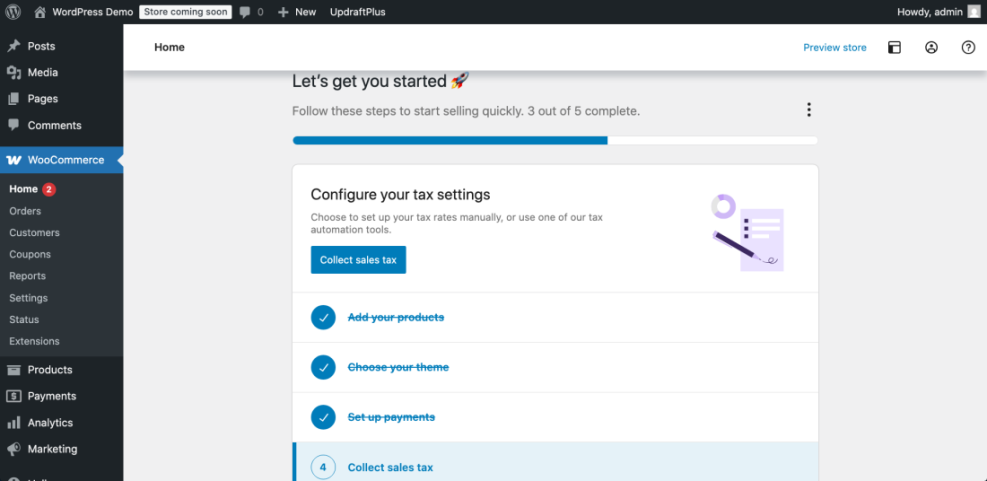 The WooCommerce dashboard in WordPress guides users through configuring tax settings for their online store.
The WooCommerce dashboard in WordPress guides users through configuring tax settings for their online store.
After activation, WordPress creates new pages for Shop, Cart, Checkout, and My account. You can add these to your menus and design them through your theme or page builder.
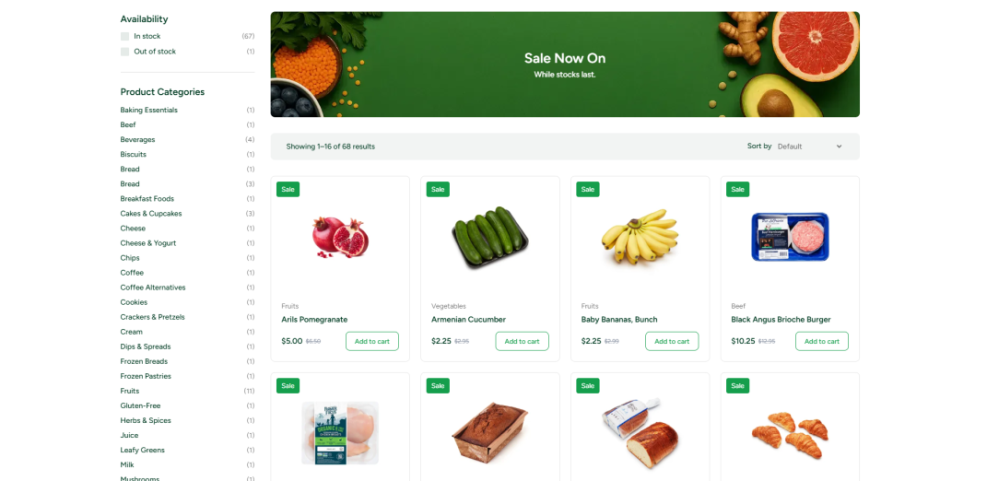
To verify WooCommerce is working, visit your new Shop page on the front end and confirm you see product grid placeholders. Then add a test product and walk through checkout using a test payment method.
Conclusion You Are Ready to Go
The key difference is simple. WordPress is the core website platform that runs everything, while WooCommerce is an ecommerce plugin that turns a WordPress site into an online store. You can run WordPress alone for blogs and business sites, or combine WordPress and WooCommerce when you need carts, checkout, and product management.
Now that you understand the roles of each, you can confidently decide whether your next project needs only WordPress, WordPress plus WooCommerce, or WordPress plus a different ecommerce solution.
Further Reading
- What is managed WordPress
- Is WordPress good for seo
- WordPress seo complete beginners guide
- Install WooCommerce Guide
- Step-By-Step Guide To Launching A WooCommerce Store





