WordPress Speed Optimization Checklist – Quick Wins for Busy Site Owners
Time saving steps to keep your site fast

Speed optimization can feel overwhelming when you already juggle content, customers, and emails every day. A slow site quietly hurts conversions, ad revenue, and even your search rankings, yet finding the time to fix it is hard.
This checklist gives you a clear order of actions so you focus on what moves the needle first. You will see which tasks you can do in minutes, which ones to schedule later, and which jobs are worth delegating to your host or developer.
WordPress Speed Optimization Quick Wins
If you are short on time, focus on the few actions that deliver the biggest speed jump. For most WordPress sites, better hosting, proper caching, and smaller images solve the majority of performance problems.
- Move to a reputable, performance focused WordPress host.
- Install and configure a proven caching plugin from your host’s approved list.
- Compress large images and convert future uploads to WebP where possible.
- Remove heavy themes, unused page builders, and abandoned plugins.
- Enable a CDN if most visitors come from different regions.
- Clean old post revisions, trashed items, and expired transients from the database.
- Update WordPress core, plugins, and themes after taking a backup.
When you follow this checklist in order, you tackle the most common bottlenecks first instead of chasing tiny optimizations that barely move your load time.
What Are the Fastest Speed Wins?
The fastest wins usually come from three areas: hosting quality, caching, and image size. A better host reduces server response time, caching cuts repeat load times, and lighter images shrink page weight. Together, these changes can take a slow home page and cut seconds from its first meaningful paint.
Checklist for the Next 60 Minutes
- Run a baseline speed test on your home page and one key landing page.
- Enable or install caching, then clear and warm the cache.
- Compress images on those two pages, especially large hero images.
- Turn off one or two obviously unused plugins and retest speed.
This quick session gives you a clear before and after, so you know whether further work should focus on hosting, media, or plugins.
When Should You Ask for Help?
You should get help when basic changes do not improve results, or when uptime and speed issues keep coming back. A developer or managed hosting provider can diagnose slow queries, misconfigured servers, and plugin conflicts that tools cannot fix alone, while you keep your attention on running the business.
Measure and Understand Your Site Speed
Before you change anything, you need to know how slow the site is and why. Free tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest show load time, Core Web Vitals, and the main causes of delay.
How Do You Run a Simple Speed Test?
Open a speed test tool in a browser tab, paste your home page URL, and choose a test location close to your main audience. Run several tests and look at the median result instead of one outlier. Then repeat the same process for a key blog post or sales page to see how performance differs across templates.
Speed Metrics Busy Owners Should Watch
As a busy site owner, you do not need to memorize every metric. Focus on three: server response time, Largest Contentful Paint, and Interaction to Next Paint. If response time is high, look at hosting. If LCP and INP are poor, images, fonts, or JavaScript are usually the problem.
From the Dashboard, go to Tools » Site Health and open the Performance section to see WordPress’ own checks.
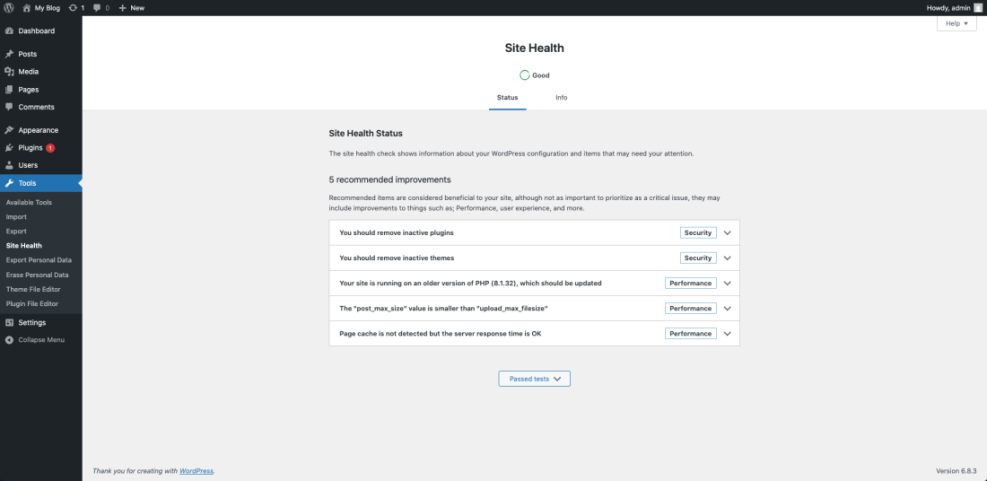
Once you understand where time it is spent, each later step in this checklist becomes easier to prioritize and justify.
Fix Hosting and Server Bottlenecks
Your hosting plan and Sever Bottlenecks sets the ceiling for how fast your WordPress site can become. Even perfect caching cannot fully fix an overloaded shared server or an outdated PHP version.
Hosting Choices That Affect Load Time
Look at four things on your current host: server location, PHP version, resource limits, and built in performance features such as server level caching. Many hosts let you switch to PHP 8 or higher with a single setting, which usually gives a noticeable performance boost.
Open your hosting panel and navigate to the section that controls PHP Settings or Software, then check which version your account uses.
Shared vs. Managed WordPress vs. VPS
The table below gives a simple comparison to help you decide whether staying on shared hosting still makes sense.
| Plan Type | Typical Speed | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shared Hosting | Slow to moderate | Very small sites | Cheap, but noisy neighbors and limited resources. |
| Managed WordPress | Fast and stable | Growing business sites | Includes caching, updates, and expert support. |
| VPS or Cloud | Very fast | High traffic or complex sites | Most flexible, but needs more technical management. |
When your site earns money or generates leads, managed hosting often pays for itself by reducing lost visits and downtime.
When Should You Switch Hosts?
Consider switching hosts when your server response time stays high even after caching, or when support keeps blaming plugins without offering real diagnostics. Frequent timeouts, slow backups, and strict resource limits are other red flags. A test site on a modern managed host can quickly show whether hosting is your main bottleneck.
Streamline Themes Plugins and Code
Heavy themes and plugin bloat often slow WordPress more than anything else. Every extra feature adds CSS, JavaScript, and database calls that browsers have to load and process.
How Many Plugins Are Too Many?
The number of plugins matters less than what they do, yet a long list often signals trouble. Dozens of overlapping marketing, page builder, or slider plugins usually mean duplicated scripts and styles. If speed feels poor, treat any plugin you do not truly need as a candidate for removal or replacement.
Audit and Remove Heavy Plugins
- List your plugins and mark anything you do not recognize or use often.
- Replace multi purpose sliders and page builders with lighter blocks where possible.
- Turn off one plugin at a time and retest to see its impact on load time.
- Delete deactivated plugins to close security gaps and reduce clutter.
From the Dashboard, go to Plugins » Installed Plugins and filter by Inactive to quickly spot tools you can remove.
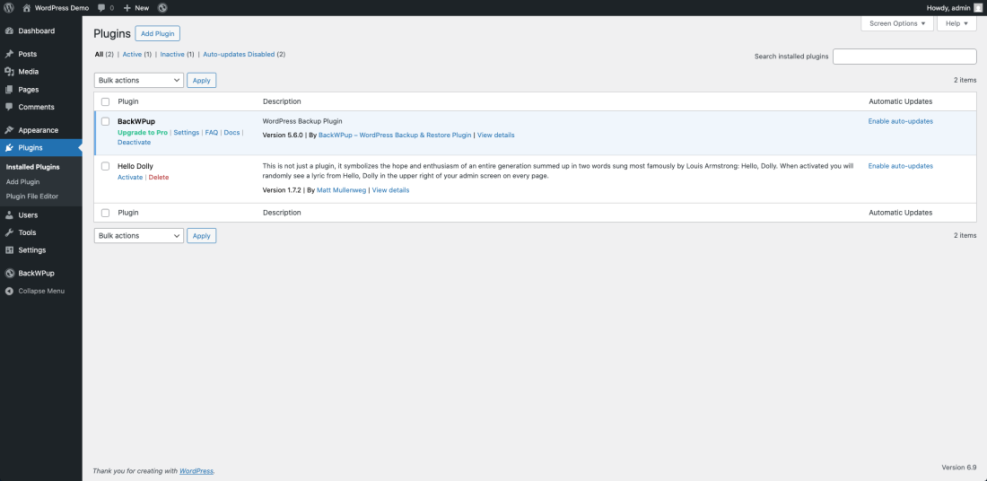
As you streamline, you may decide to move complex features to custom code or a single well supported plugin instead of several overlapping ones.
Disable Unused Features Safely
Some plugins and themes load extras such as emojis, dashicons, and block styles on every page. You can disable a few of these in your theme’s functions.php file or a small must use plugin.
// Disable WordPress emoji scripts and styles.
add_action( 'init', function() {
remove_action( 'wp_head', 'print_emoji_detection_script', 7 );
remove_action( 'wp_print_styles', 'print_emoji_styles' );
}
Always test code changes on a staging site first, and take a backup so you can roll back if you see layout issues.
Optimize Images Fonts and Media
Large images and font files are often the biggest files on a WordPress page. Therefore, shrinking them gives you an immediate drop in page weight without touching design.
Which Images Hurt Performance Most?
The worst offenders are usually full width hero images, background photos, and large logos uploaded straight from a camera or design tool. When these files are several megabytes each, they dominate your waterfall chart. Optimizing just a few visual elements can dramatically improve Largest Contentful Paint and perceived speed.
Compress and Resize Images in Batches
Install a trusted image optimization plugin that compresses existing uploads and converts new images to modern formats like WebP. Set maximum widths that match your theme’s content area so you do not serve huge files into small spaces.
From the Dashboard, open Media » Library and switch to the list view to see file sizes for your largest images.
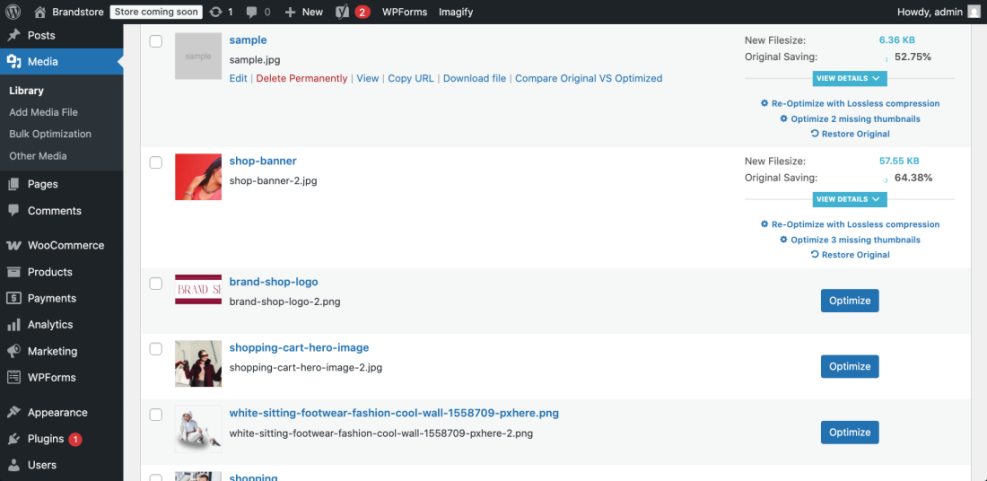
Make Fonts and Embeds Lighter
Limit the number of font families and weights you load. In many cases, one body font and one accent font are enough. For video and map embeds, consider using preview images or placeholder blocks that load the heavy iframe only after a click. This keeps initial page load lean on slower connections.
Boost Speed with Caching and CDN
Caching stores ready made HTML versions of your pages so they load quickly for the next visitor. A content delivery network serves static files like images, CSS, and JavaScript from servers closer to your users.
What Does a Caching Plugin Actually Do?
A caching plugin saves a generated copy of each page and serves it directly instead of running WordPress for every visit. Many tools also enable browser caching, compression, and file minification. This reduces database queries and PHP work, so your server can handle more traffic with the same resources.
Recommended Caching Settings for Non-Tech Users
- Enable page caching for all public pages, not for admin screens.
- Turn on browser caching and GZIP or Brotli compression.
- Use automatic cache preloading so popular pages stay warm.
- Avoid combining files if it breaks layouts or third party scripts.
From the Dashboard, go to your caching plugin menu, such as Settings » Cache, and look for options labeled Page cache, Browser cache, and Preload.
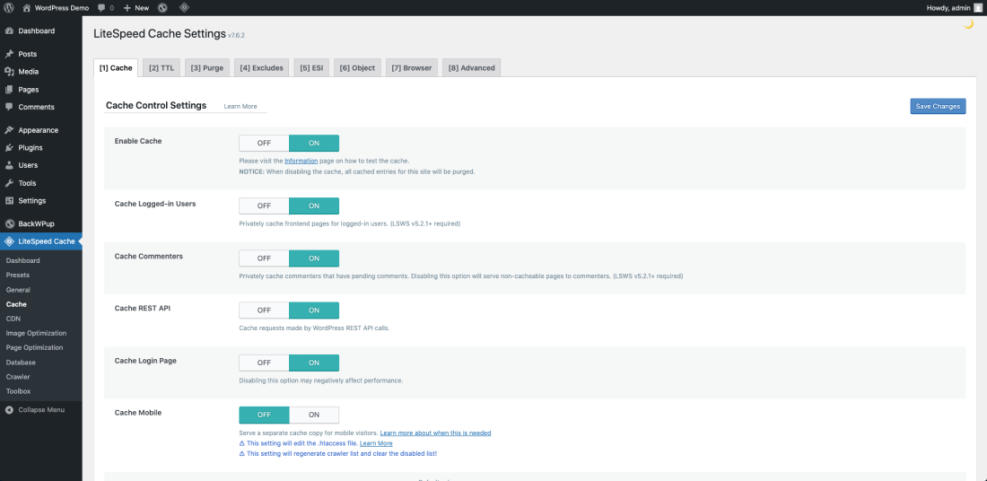
Simple CDN Setup Steps
- Sign up for a reputable CDN service or enable the CDN option inside your host.
- Point your DNS or CDN hostname according to their setup guide.
- Connect the CDN to WordPress using your caching plugin or a small integration plugin.
- Test a few pages to confirm that images and static assets now load from the CDN domain.
If your audience is global, a CDN can remove hundreds of milliseconds of latency and smooth out performance spikes during traffic peaks.
Clean and Optimize Your Database
Over time, WordPress stores post revisions, transient data, and logs that you no longer need. Removing this clutter keeps queries lean and can reduce backup size.
Why Does the Database Slow WordPress?
A bloated database forces MySQL to scan more rows and indexes for every request. When tables contain thousands of old revisions, spam comments, or expired sessions, queries take longer and lock resources. Cleaning this data reduces a silent source of latency that caching cannot always hide.
Safe Ways to Clean Overhead Data
Use a well known optimization plugin that offers one click cleanup of revisions, trashed posts, spam comments, and transient options. Always uncheck anything related to user data or orders if you run ecommerce. Then run the cleanup when traffic is low so maintenance does not overlap with peak visits.
From the Dashboard, visit Tools » Database or the settings page of your optimization plugin to review which tables can be cleaned safely.
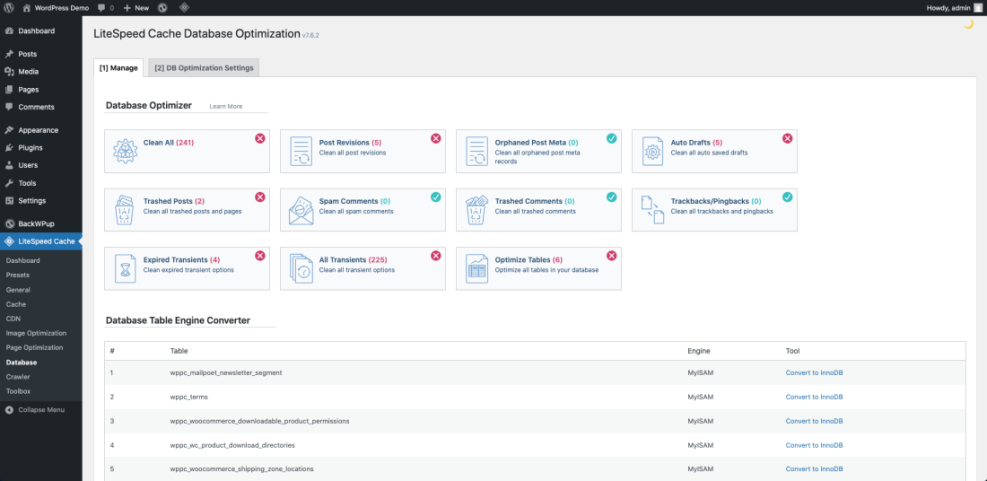
Schedule Automatic Cleanups
Most database tools let you schedule regular cleanups weekly or monthly. Set a reasonable schedule, then monitor site behavior for a few weeks. If logs show no issues, you can leave that automation in place and treat database health as one less task to remember.
Ongoing Maintenance for Lasting Speed
Speed optimization is not a one time project. Theme updates, new plugins, and fresh content all change how your pages load over time.
Monthly Speed Maintenance Checklist
- Re run speed tests for your home page and one key landing page.
- Update WordPress core, plugins, and themes after taking a backup.
- Remove any plugins you installed but no longer need.
- Clean the database and clear expired cache entries.
- Review new images to ensure they follow your compression rules.
To track trends over time, note your key metrics in a simple spreadsheet so you can spot slowdowns before users complain.
How Often Should You Retest Performance?
Retest performance after any major change such as switching themes, adding a marketing suite, or moving hosts. In addition, schedule a quick test once per month even if nothing big changed. Regular checks help you detect slowdowns early, before they start to hurt conversions and search traffic.
WordPress Speed Optimization Conclusion
WordPress speed optimization does not require you to become a developer. When you improve hosting, add smart caching, trim plugins, and shrink media, you handle the same bottlenecks professionals focus on every day.
Choose one section of this checklist to complete this week and record your new load time. Then treat the remaining sections as a simple roadmap. When the workload grows, you can delegate individual tasks or even full sections while still keeping control of priorities and results.
If you want a deeper dive into specific areas, consider planning content on topics such as Beginner guide WordPress speed core web vitals or Caching plugin comparisons WordPress performance so you can continue improving performance steadily.
More WordPress Guides You Might Like
To continue improving your site without wasting time, explore these related topics in your content plan.
- How to choose the best WordPress hosting
- Beginner guide to WordPress speed optimization
- WordPress speed optimization step by step
- Beginner guide WordPress speed core web vitals
These ideas help you break WordPress Speed Optimization into focused projects you can handle between campaigns, launches, or client work.





