
If your site feels WordPress slow and unresponsive, every page load can frustrate visitors and hurt your rankings. The good news is that WordPress itself is rarely the only problem. Most slowdowns come from hosting, themes, plugins, and media that you can control.
In this guide you will understand the main reasons WordPress becomes slow, learn how to diagnose each bottleneck, and follow clear steps to fix them. By the end, you will know how to measure performance, remove the biggest speed killers, and move toward a fast, stable WordPress site.
Quick Overview of Ways to Fix a Slow WordPress Site
| Method | Where You Use It | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Change Password from Profile | WordPress dashboard » Users » Profile / All Users | Safely update your own or another user’s password when you can already log in to the WordPress dashboard. |
| Reset Forgotten Password by Email | WordPress login page » “Lost your password?” link | Recover access when you forgot your password but still have access to the email address linked to your WordPress account. |
| Reset Password in Database (phpMyAdmin) | Hosting control panel » phpMyAdmin » wp_users table | Emergency method for changing a password directly in the database when email resets fail and you’re locked out of the site. |
| Change Password with WP-CLI | SSH terminal with WP-CLI installed | Fast, scriptable password updates for developers or power users managing multiple sites or user accounts from the command line. |
| Secure Account After Password Change | WordPress dashboard » Profile & Security/2FA plugin settings | Add two-factor authentication, log out other sessions, and clean up user roles so your new password and login stay secure long term. |
What You Need to Fix a Slow WordPress Site
- Access to your WordPress Admin Dashboard with an administrator account.
- Login details for your web hosting control panel or cPanel.
- A recent full site backup using your preferred Backup Plugin or hosting tools.
- Basic familiarity with installing and updating WordPress plugins.
- Optional access to performance tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights and GTmetrix.
Step 1: Fix WordPress Slow Hosting Environment Issues
How Slow Hosting Makes WordPress Lag
Your hosting server is often the biggest reason WordPress feels slow. If the server is overloaded or outdated, no amount of optimization will fully fix performance.
- Log in to your hosting Control Panel or cPanel.
- Locate your resource usage section, often under Metrics or Statistics.
- Check CPU, RAM, and I/O usage to see if your site frequently hits limits.
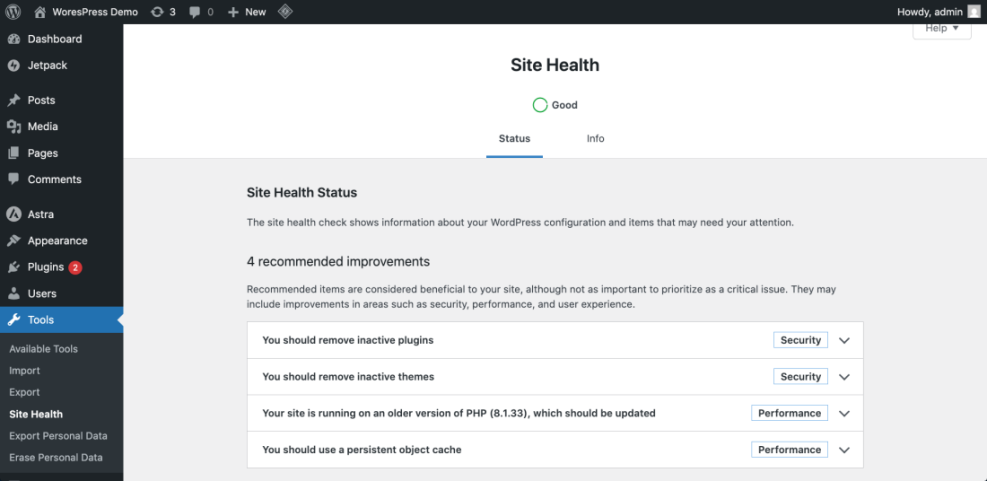
- In WordPress, navigate to Tools » Site Health and open the Info tab to review server and database versions.
- Note if you are on old PHP versions or shared hosting plans with heavy resource limits.
Navigate to Tools » Site Health and open the Status tab to review performance recommendations.
To verify hosting is a bottleneck, test your site with a speed tool and pay attention to Time To First Byte (TTFB). If TTFB is very high, consider following How To Choose Fast WordPress Hosting and Best WordPress Hosting for Beginners for upgrade options.
Step 2: Audit Slow WordPress Themes and Page Builders
Choosing a Lightweight Theme to Speed Up WordPress
Heavy themes and page builders add extra CSS, JavaScript, and layout logic that can make WordPress slow, especially on mobile.
- From your dashboard, go to Appearance » Themes.
- Identify your active theme and check if it is marketed as lightweight or performance focused.
- Navigate to a slow page on the front end and open your browser’s Developer Tools network tab.
- Reload the page and look at the number and size of CSS and JS files loaded from the theme and page builder.
- Temporarily switch to a default theme such as Twenty Twenty-Four and test the same page speed to compare.
Open the slow page, right click, and choose Inspect then select the Network tab to view file requests.
If your pages become much faster on a default theme, follow guidance from How to Choose a Lightweight WordPress Theme before committing to a redesign.
Step 3: Reduce Heavy WordPress Plugins and Third-Party Scripts
Removing Plugin Bloat That Makes WordPress Slow
Too many plugins and external scripts can make WordPress slow by adding extra database queries, HTTP requests, and blocking JavaScript.
- In your dashboard, open Plugins » Installed Plugins.
- Make a list of all active plugins, especially page builders, sliders, social share tools, and analytics add-ons.
- Deactivate non essential plugins one by one and test your site speed after each change.
- Remove plugins that duplicate features already covered by your theme or other plugins.
- Review third party scripts such as chat widgets, ad networks, and marketing pixels configured in Appearance » Customize or your SEO plugin settings.
Use a speed testing tool and view the Waterfall chart to identify slow third party domains.
After cleanup, your total number of requests and overall page size should drop, improving load times and Core Web Vitals.
Step 4: Optimize Images to Speed Up a Slow WordPress Site
Resizing and Compressing Media for Faster WordPress Pages
Uncompressed images are a classic reason WordPress becomes slow, especially on mobile and image heavy blogs.
- Go to Media » Library and switch to the List view to see file sizes.
- Sort by file size if your media library plugin allows it, or manually scan for very large images.
- Install a reputable image compression plugin from Plugins » Add New.
- Use the plugin’s bulk optimization tool to compress existing images.
- Configure the plugin to generate modern formats such as WebP where supported.
Open one slow blog post and run Google PageSpeed Insights to view the recommendation for Properly size images.
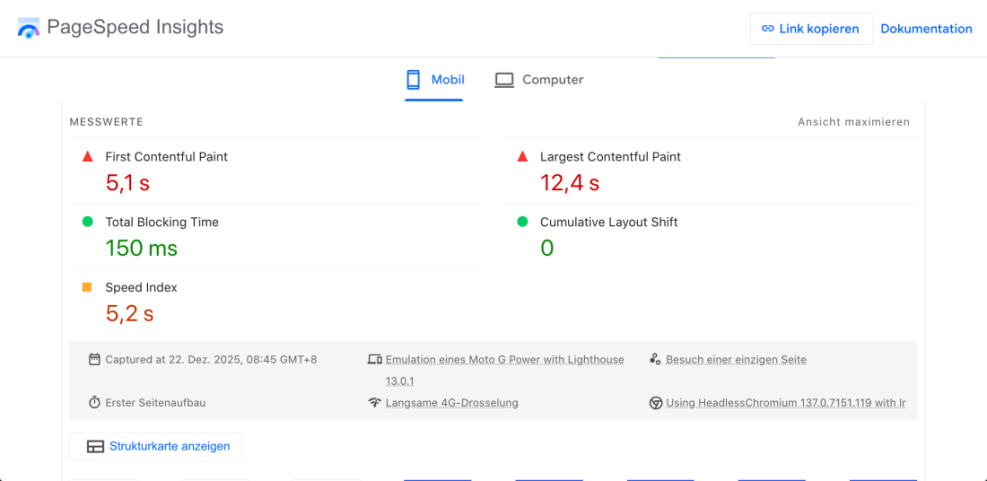
For a full workflow, follow Image Optimization For Faster WordPress Sites and Step by Step Image Optimization for WordPress to keep new uploads lean.
Step 5: Enable Caching and a CDN to Speed Up WordPress
Caching Options to Fix Slow WordPress Load Times
Without caching, WordPress generates every page from scratch on each visit, which can make the site slow under even moderate traffic.
- From the dashboard, go to Plugins » Add New and search for a reputable Caching Plugin.
- Install and activate the plugin, then open its settings from Settings or its own menu item.
- Enable basic page caching and browser caching, following the plugin’s recommended safe defaults.
- If your host offers server level caching, enable it from your hosting control panel instead of overlapping with conflicting options.
- Set up a Content Delivery Network by following CDN Setup or How to Use a CDN with WordPress Blogs.
Navigate to your caching plugin’s Dashboard or Status page to confirm that caching is active.
Re test your site with a speed tool and you should see improved repeat load times and better performance scores.
Step 6: Clean Up the Database to Fix Slow WordPress Performance
Database Optimization for a Slow WordPress Site
Over time, post revisions, transients, and scheduled tasks can bloat the database and make WordPress slow on certain actions.
- Install a trusted database optimization plugin from Plugins » Add New.
- Go to the plugin’s settings page under Tools or Settings.
- Select options to clean up post revisions, trash, and expired transients only.
- Run a manual optimization and monitor database size in your hosting control panel.
- Use a plugin or monitoring tool to inspect WP Cron tasks and remove those left behind by old plugins.
In your hosting phpMyAdmin or database manager, refresh the database size view after optimization.
For a cautious workflow, follow Database Optimization Basics For Faster And Safer WordPress Sites before making large changes.
You can also limit stored revisions with a simple configuration tweak in wp-config.php:
define( 'WP_POST_REVISIONS', 10 );After cleanup, dashboard actions like editing posts and running queries should feel more responsive.
Step 7: Improve Core Web Vitals for a Slow WordPress Site
Using Core Web Vitals to Measure WordPress Slowness
Even if your site feels faster, poor Core Web Vitals can still make WordPress slow in the eyes of search engines and users.
- Open Google Search Console and navigate to Page Experience or Core Web Vitals.
- Review problem URLs for metrics like LCP, FID, and CLS.
- Run the worst pages through PageSpeed Insights and scroll to the Opportunities section.
- Address specific issues such as render blocking resources, unoptimized fonts, or layout shifts.
- Compare your results with the guidance in Core Web Vitals Optimization for WordPress.
Use the Mobile tab in PageSpeed Insights to see how real users experience your site on phones.
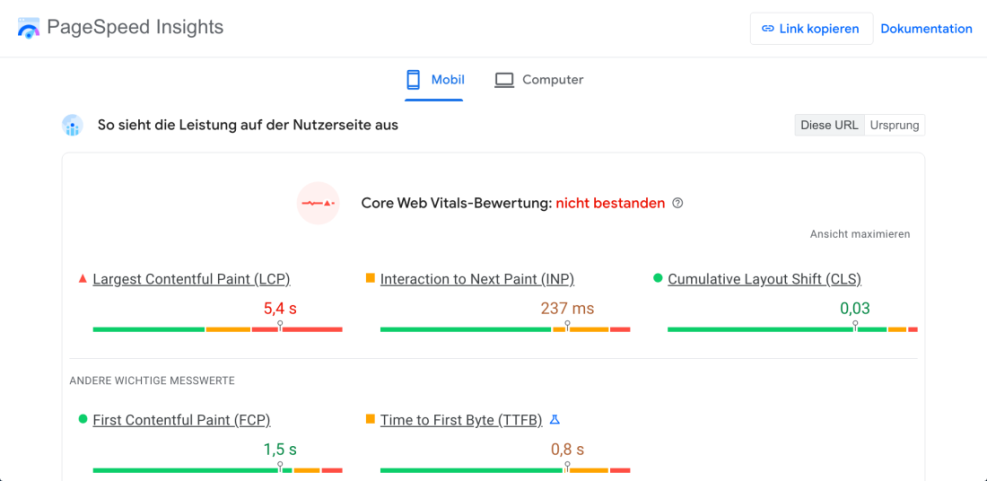
As you fix issues, your pages should move from poor to good status in both Search Console and speed tools, confirming that your improvements are working.
Step 8: Monitor WordPress Speed Over Time
Tracking Slow WordPress Issues Before They Return
WordPress can become slow again as you add plugins, content, or traffic. Ongoing monitoring helps you catch new bottlenecks early.
- Set up uptime and performance monitoring following Monitoring Uptime and Performance for WordPress.
- Schedule recurring tests in tools like GTmetrix or WebPageTest for key pages.
- Review your plugin and theme changes monthly and remove anything no longer needed.
- Use a simple maintenance checklist such as WordPress Maintenance Checklist For Busy Site Owners.
- Document major site changes so you can correlate them with any speed drops.
Check your monitoring dashboard at least once per week to confirm there are no spikes in load time or error rates.
Over time, this routine will help you keep WordPress fast instead of waiting until performance becomes a crisis.
Conclusion: Fixing a Slow WordPress Site for Good
Now you know that a WordPress slow site is usually the result of several bottlenecks working together, not just the core software. You reviewed hosting limits, theme and plugin bloat, image sizes, caching, database health, and Core Web Vitals.
By following these steps and using the linked resources, you can systematically remove each cause, verify improvements with real data, and keep your WordPress site fast for both visitors and search engines.





