What is WordPress SEO
A beginner-friendly explanation of how SEO works in WordPress and what you actually need to do

People often hear that “WordPress is SEO friendly out of the box” and assume that installing WordPress is all it takes to rank in Google. In reality, WordPress SEO is about using WordPress in a way that helps search engines understand, crawl, and trust your site – and that requires a bit of setup.
In this guide, you’ll learn what “WordPress SEO” actually means, how it connects to general SEO best practices, and the specific settings, plugins, and habits you should focus on inside your WordPress dashboard. We’ll walk from foundational settings all the way to measuring your organic traffic so you know whether your work is paying off.
If you’re completely new to WordPress itself, you may also want to review the overall WordPress guides and tutorials overview so you’re comfortable with the dashboard, themes, and plugins before diving deep into SEO.
What Does WordPress SEO Actually Mean?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving your website so it shows up higher and more often in search engines like Google. WordPress SEO is simply SEO applied to a WordPress website, using WordPress-specific tools and settings.
On a WordPress site, SEO typically includes three big areas:
- Technical SEO: making sure your site loads fast, is secure (HTTPS), mobile friendly, and easy for search engines to crawl and index.
- On-page SEO: optimizing titles, meta descriptions, headings, URLs (slugs), and content so every page answers a clear search intent.
- Content & structure: organizing your posts, pages, categories, and internal links in a way that’s easy for both people and search engines to understand.
WordPress helps with SEO by giving you a clean CMS, permalinks, themes, and plugins. But none of those automatically “do SEO” for you. WordPress SEO is about how you configure WordPress and how you publish content inside it.
Prerequisites
Before you start tweaking WordPress SEO settings, make sure you have the basics in place:
- A working WordPress site (self-hosted WordPress.org or a Business plan on WordPress.com).
- Administrator access to the WordPress dashboard.
- A modern, responsive theme (for example, the Jannah theme) that is kept updated.
- Basic familiarity with posts vs pages, categories vs tags, and how to create or edit content.
Step 1: Make Your WordPress Site Search-Engine Friendly
Your first WordPress SEO task is to make sure you aren’t accidentally blocking search engines and that your URLs are clean and readable.
1. Check the “Search Engine Visibility” setting
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Settings > Reading.
- Find the option labeled “Search engine visibility”.
- Make sure “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” is unchecked.
- Click Save Changes.
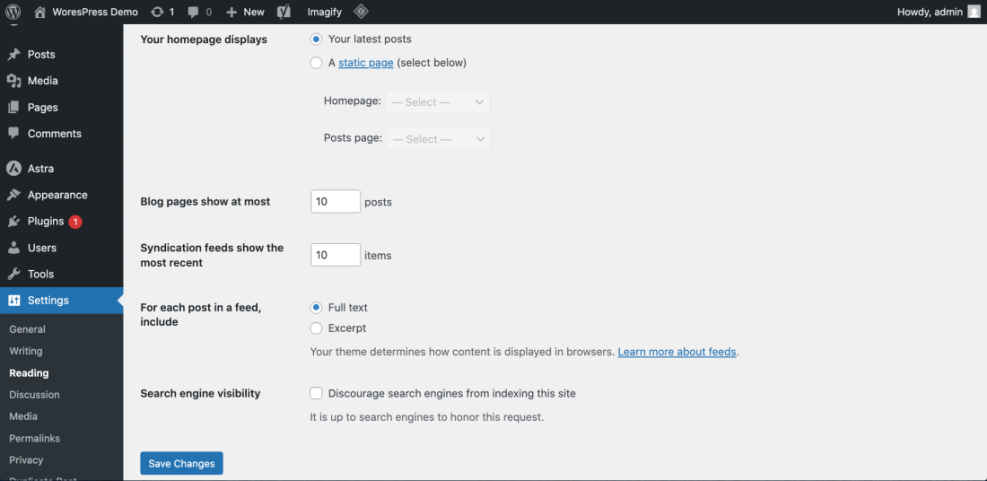
Checkpoint: If that box was checked, Google may have been told not to index your site. Once you uncheck it, it can take days or weeks for search engines to crawl again, but at least they’re no longer blocked.
2. Use SEO-friendly permalinks
- Go to Settings > Permalinks.
- Select the Post name option so your URLs look like
/sample-post/instead of numbers or dates. - Click Save Changes.
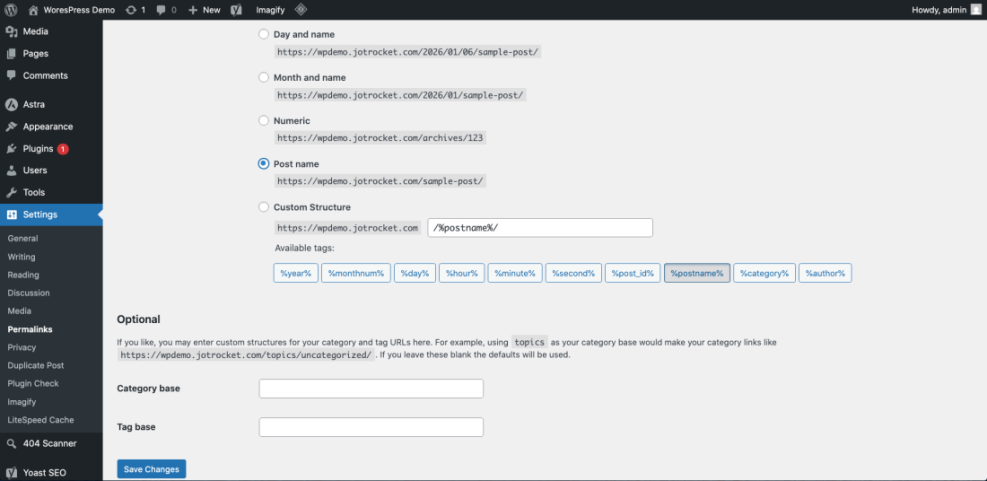
Checkpoint: New posts and pages will now use clean, descriptive URLs that match your titles. This makes it easier for users to read and for Google to understand your content.
Step 2: Install an SEO Plugin and Configure Core Settings
WordPress doesn’t include advanced SEO tools like XML sitemaps, meta tags, and schema markup by default. That’s where SEO plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or All in One SEO come in.
1. Install a reputable SEO plugin
- Go to Plugins > Add New in your dashboard.
- Search for a popular SEO plugin such as “Yoast SEO”.
- Click Install Now, then Activate.
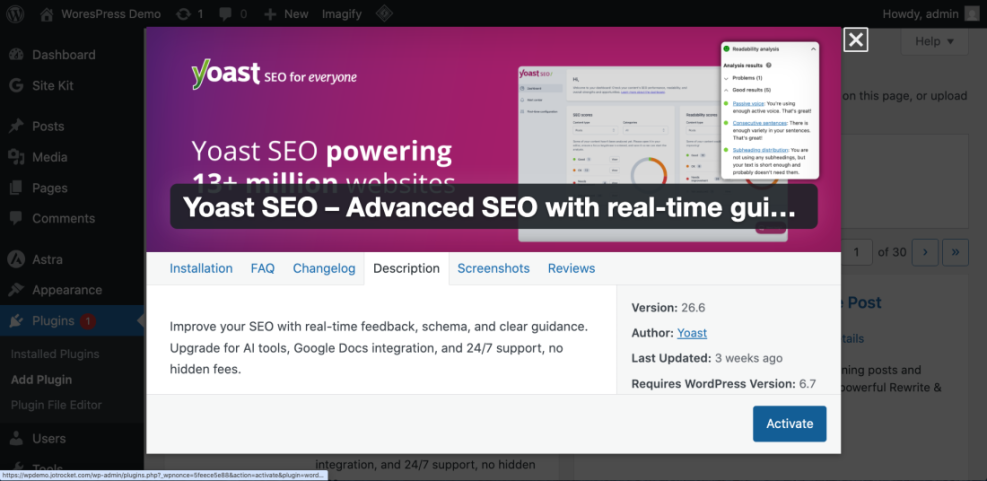
2. Run the plugin’s setup wizard
Most SEO plugins include a setup wizard that guides you through key options:
- Site type (blog, business, online store, etc.).
- Whether your site is live or under construction.
- Search appearance for posts, pages, and archives.
- XML sitemaps and basic schema settings.
Follow the wizard carefully, but don’t stress about getting everything perfect. You can adjust settings later as you learn more.
If you choose Yoast SEO, you can follow a more detailed walkthrough using the Yoast SEO setup guide once you’re comfortable with the basics.
Checkpoint: After setup, your plugin should be generating an XML sitemap and adding proper meta tags for search engines on each page.
Step 3: Optimize Individual Posts and Pages for WordPress SEO
Once your site-level settings are ready, most of your WordPress SEO work happens when you create or update content. Each post or page is a chance to answer a specific search question.
1. Choose a clear focus for each page
Before you start writing, decide what search phrase (or topic) that page should target. This doesn’t have to be an exact-match keyword, but it should represent the main question your content answers.
2. Use the Classic Editor fields effectively
- Enter a descriptive post title that includes your main phrase naturally.
- Write your content in the editor using headings (
<h2>,<h3>) to break sections into clear topics. - Scroll to your SEO plugin’s meta box (e.g., Yoast SEO) below the editor and customize:
- SEO title (what shows in search results).
- Slug (the final part of the URL – short and descriptive).
- Meta description (1–2 sentences that make users want to click).
3. Add internal links and image alt text
- Link to other relevant posts and pages so users and search engines can discover related content.
- When you upload images, fill in the Alt Text field to describe what the image shows (and when relevant, how it relates to the topic).
If you want a detailed publishing checklist you can follow every time you publish a new article, see the beginner checklist for optimizing WordPress blog posts.
Checkpoint: Each important page on your site should have a clear focus, a good SEO title and description, readable headings, and at least a couple of internal links to and from other pages.
Step 4: Strengthen the Technical Foundations of Your WordPress SEO
Even the best content can struggle to rank if your site is slow, unstable, or hard to crawl. Technical SEO is about giving your content a solid foundation.
1. Improve performance and Core Web Vitals
- Use quality hosting and a recent PHP version to reduce server response time.
- Install and configure a caching plugin (e.g., page cache + browser cache).
- Optimize images before upload to keep file sizes small.
- Limit heavy page builders and unnecessary scripts on each page.
On many sites, these changes alone lead to noticeable speed improvements and better user engagement.
2. Ensure mobile friendliness
- Use a responsive theme so your layout adapts to phones and tablets.
- Test your main pages on actual mobile devices and fix layout issues.
- Avoid tiny buttons, overlapping elements, or popups that cover the content.
3. Keep your site secure and stable
- Use HTTPS with a valid SSL certificate.
- Keep WordPress core, themes, and plugins up to date.
- Remove unused plugins and themes that expand your attack surface.
You can also use WP-CLI (if your host supports it) to clear cache or update plugins from the command line:
# Run this in your SSH terminal
wp plugin update --all
wp cache flush
Checkpoint: A technically sound WordPress site loads quickly, is mobile-ready, and stays online without frequent errors – all of which support better SEO results.
Step 5: Measure and Improve Your WordPress SEO Over Time
SEO is not a one-time switch; it’s an ongoing process. The good news is that WordPress makes it relatively easy to measure changes and refine your strategy.
1. Connect to Google Search Console
- Verify your site in Google Search Console.
- Submit your XML sitemap URL (usually created by your SEO plugin).
- Review the coverage reports to see which pages are indexed and where errors exist.
2. Track traffic and engagement
- Connect Google Analytics (or another analytics tool) to monitor organic traffic.
- Watch metrics like sessions, bounce rate, and pages per session on your key posts.
- Identify posts that get impressions but low click-through rate, and improve their titles and meta descriptions.
3. Refresh and expand content
- Update older posts with fresh information, better formatting, and new internal links.
- Add FAQs or short sections that address related questions users search for.
- Keep publishing new, helpful content that fits your overall site structure.
Checkpoint: Over time you should see more keywords, more impressions, and more clicks from organic search as you consistently apply good WordPress SEO practices.
Turn “WordPress Is SEO Friendly” Into a Real Strategy
WordPress SEO isn’t a mysterious plugin setting or a single checklist. It’s the combination of a search-friendly setup, a well-configured SEO plugin, high-quality content, and a technically solid site that loads fast and stays secure.
By making your site indexable, installing and configuring an SEO plugin, optimizing every post you publish, and improving your performance and security, you give search engines every reason to crawl, understand, and trust your pages. From there, consistent content and ongoing measurement help you grow your organic traffic over time.
Start with the basics in this guide, then deepen your skills with more specialized tutorials on SEO plugins, internal linking, and performance optimization as your site grows.
Further Reading
- WordPress SEO Complete Beginner’s Guide
- Best WordPress SEO Plugins and Tools
- How to Do SEO for a WordPress Website
- Internal Linking Strategies for WordPress





