How to Improve SEO on WordPress
A practical, step-by-step checklist to boost your WordPress rankings from inside your dashboard.

If your WordPress site is live but barely getting any Google traffic, you are not alone. Many site owners install an SEO plugin, click a few buttons, and then wonder why their rankings barely move.
This guide shows you exactly how to improve SEO on WordPress using a practical, repeatable workflow. You will benchmark your current results, fix structural issues, optimize content, improve internal links, and apply speed and technical quick wins—all using tools available right inside your WordPress dashboard.
If you are completely new to the topic, start with our WordPress SEO complete beginner’s guide, then come back here when you are ready to work through a hands-on optimization checklist.
Prerequisites
Before you start changing settings or updating posts, make sure you have a safe environment and the right access.
- Admin-level access to your WordPress dashboard.
- A recent backup of your WordPress site (files + database).
- At least one SEO plugin installed and active (Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or similar).
- Access to basic analytics (Google Analytics, Site Kit, or a similar stats tool).
- Access to Google Search Console for your domain (recommended).
Step 1: Benchmark Your Current WordPress SEO
Never optimize blindly. You need a baseline so you can confirm which changes are actually working.
- Check organic traffic trends. In your analytics tool, filter traffic by “Organic Search” for the last 3–6 months. Note whether it is flat, declining, or growing.
- Review top pages and queries. In Google Search Console, open Performance → Search results and sort by Clicks or Impressions. Identify:
- Pages already getting impressions but low clicks (CTR problem).
- Pages with clicks but average position worse than 10 (ranking opportunity).
- Scan a few posts in your SEO plugin. Open some key posts and check the plugin’s SEO/readability analysis. Look for missing meta descriptions, weak titles, or absent focus keywords.
Step 2: Fix Your Site Structure and Permalinks
Google prefers clean, logical site structures. WordPress makes this easy, but only if you configure it correctly.
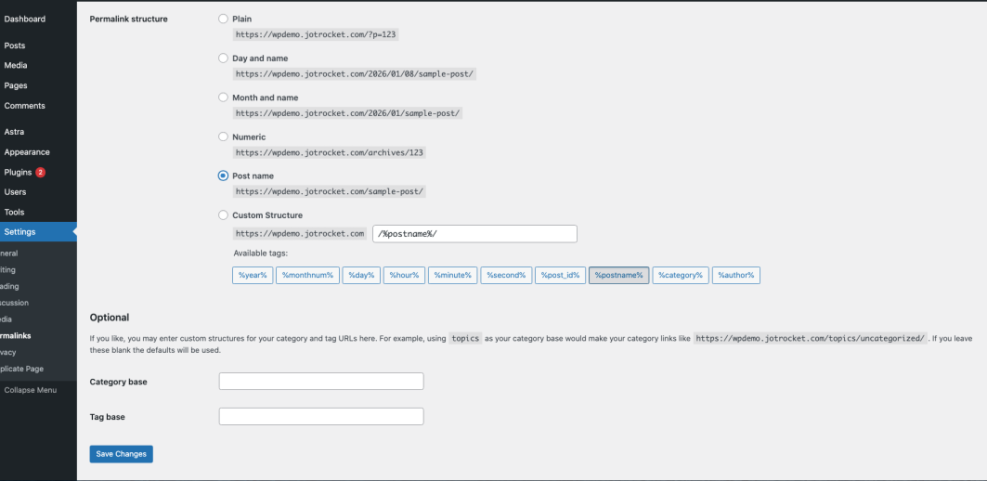
2.1 Set SEO-friendly permalinks
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Settings → Permalinks.
- Select the Post name option.
- Click Save Changes.
2.2 Clean up categories and tags
Messy categories and tags confuse both users and search engines. Aim for a small, focused taxonomy.
- Merge near-duplicate categories (for example, “SEO Tips” and “SEO Advice”).
- Delete empty or irrelevant tags that are only used once and bring no traffic.
- Make sure each post belongs to one primary category that clearly describes its topic.
2.3 Improve navigation and key pages
- Ensure your main menu links to your most important sections (services, key blog categories, contact page).
- Check that every page is reachable within 3 clicks or fewer from the homepage.
- Add a clear “Blog” or “Resources” link to help both users and crawlers discover content.
Step 3: Optimize Your Content Around the Right Keywords
Most WordPress SEO wins come from improving content you already have. For each important post, run a focused on-page SEO pass.
3.1 Choose or confirm a main keyword
- Use your favorite keyword tool or Google’s autocomplete/related searches to find a phrase that:
- Matches the intent of the post.
- Has reasonable search volume.
- Is not too competitive for your site’s current authority.
- Set this phrase as the Focus Keyphrase in your SEO plugin for that post.
3.2 Update titles, headings, and meta descriptions
- Make sure the SEO title includes the main keyword naturally and promises a clear benefit.
- Check that the H1 heading is unique, descriptive, and closely related to the SEO title (but not necessarily identical).
- Write a compelling meta description that:
- Uses the keyword once.
- Explains what the reader will get.
- Includes a soft call to action (e.g., “learn,” “discover,” “compare”).
3.3 Improve body content and readability
- Add a clear introductory paragraph that mentions the keyword once in a natural sentence.
- Break long blocks of text into shorter paragraphs and use subheadings (
<h2>,<h3>) to structure the page. - Use bullet points and numbered lists to make steps easy to follow.
- Add examples, screenshots, or small case studies where helpful.
If you want a deeper breakdown of every element on the page, follow our step-by-step guide to on-page SEO in WordPress after you complete this checklist.
[h3]3.4 Optimize images in each post[/h3]Within the Classic Editor or Block Editor, click each image and check:
- Alt text: Describe the image in plain language and naturally include the keyword when it truly fits.
- File name: Use descriptive names like
wordpress-seo-checklist.pnginstead ofIMG_1234.pngfor newly uploaded images. - Size: Avoid inserting huge images and then shrinking them with CSS. Upload appropriately sized images.
Step 4: Strengthen Internal Linking on WordPress
Internal links help Google understand which pages on your site are most important and how topics relate to each other. They also keep readers on your site longer.
4.1 Add contextual internal links in posts
- Open one high-value post in the editor.
- Highlight a relevant phrase in the content (for example, “WordPress speed optimization”).
- Click the Insert/edit link button in the editor toolbar.
- Search for and select another relevant post that adds depth to that topic.
- Repeat this for 3–5 internal links that truly help the reader.
4.2 Add links from old posts to new ones
Most site owners only link from new posts to old content. Reverse this for extra gains.
- List your newest 5–10 posts.
- Search for older posts that mention similar topics or keywords.
- Edit those older posts and add contextual links pointing to your newer content.
Step 5: Improve Speed and Technical SEO Basics
Slow, clunky sites struggle to rank, especially on mobile. WordPress gives you many ways to speed things up without touching code.
5.1 Enable caching
- Install and activate a reputable caching plugin if you do not have one already.
- Use the plugin’s setup wizard to enable page caching and browser caching.
- Test your site after enabling caching to make sure layouts and dynamic features still work.
5.2 Optimize images site-wide
Large, uncompressed images are one of the most common performance issues on WordPress sites.
- Enable image compression and lazy loading in your performance or image optimization plugin.
- Re-upload critical images (like hero banners) at the exact display size instead of full-resolution originals.
- Use modern formats (such as WebP) when supported by your hosting and plugins.
For a dedicated workflow, see our image optimization checklist for WordPress websites once you have finished the basics.
5.3 Check mobile usability and Core Web Vitals
- Run your site through a speed testing tool and note issues related to mobile and Core Web Vitals.
- Switch to a lightweight, responsive theme if your current theme feels slow or outdated.
- Disable heavy plugins or features you do not actually use (sliders, autoplay video backgrounds, etc.).
Step 6: Configure Your WordPress SEO Plugin Correctly
Your SEO plugin is the control center for many technical SEO settings. Misconfigured options can hold you back, even if your content is strong.
6.1 Use only one main SEO plugin
- Ensure only one full-featured SEO plugin (like Yoast or Rank Math) is active.
- Deactivate and fully remove any old SEO plugins to avoid duplicate meta tags and sitemaps.
6.2 Run the setup wizard
- In your SEO plugin settings, run the Configuration Wizard or onboarding flow.
- Set your site type (blog, business site, online store, etc.).
- Configure title templates so posts automatically include your brand or site name.
6.3 Enable XML sitemaps and clean indexing
- Turn on XML sitemaps and confirm the sitemap URL is submitted in Google Search Console.
- Noindex low-value content such as tag archives you do not use, thin thank-you pages, or test pages.
- Ensure important pages (homepage, primary category pages, pillar posts) are set to be indexed.
Step 7: Build an Ongoing SEO Routine
SEO on WordPress is not a one-time project. You will get far better results by doing a little work consistently than trying to fix everything in one weekend.
- Weekly: Optimize any new post you publish (titles, meta, headings, internal links).
- Monthly: Update 2–3 older posts with fresh data, new screenshots, and better internal links.
- Quarterly: Review speed scores and plugin list, removing anything you no longer need.
- Ongoing: Watch Google Search Console for new keywords, errors, and pages with dropping clicks.
Keep Improving SEO on WordPress With a Simple System
Improving SEO on WordPress does not require magic tricks or risky hacks. By fixing your structure, upgrading your content, reinforcing internal links, speeding up your site, and configuring your SEO plugin properly, you create a strong foundation that Google can understand and reward.
Start with a small batch of your most important posts, work through each step in this checklist, and track changes in rankings and traffic. Once you see what works, scale the same process across the rest of your content library for steady, compounding SEO gains.
Further Reading
- How to Increase SEO on WordPress
- Best WordPress SEO Plugins and Tools
- Internal Linking for WordPress Beginners
- WordPress Speed Optimization Step-by-Step
- How to Add Schema Markup in WordPress





