WordPress Performance & Speed Optimization Guide
Make your WordPress site load faster for visitors

WordPress speed optimization helps your site load quickly and keep visitors engaged. Slow pages frustrate people, increase bounce rates, and waste your hosting resources. When performance slips, even great content and design cannot save the experience. You want each page to feel instant, whether someone visits from a phone on mobile data or a laptop on fast Wi-Fi.
This guide shows you how to diagnose slow pages, choose the right tools, and apply practical fixes that work on real WordPress sites. You will learn how to measure performance, improve hosting and caching, optimize images and code, clean up your database, and keep Core Web Vitals in a healthy range over time.
WordPress Speed Optimization Basics
At a high level, WordPress speed optimization means reducing the time it takes for your pages to become usable for visitors. You do this by improving server response, sending fewer and smaller files, and ensuring the browser can render your content without delays. The result is a site that feels smooth, responsive, and trustworthy.
Three big levers usually create the biggest gains: quality hosting, smart caching, and optimized media. When you combine these with a lean theme and minimal plugins, you often cut load times from several seconds down to well under two. This also supports better rankings and higher conversion rates.

Before you start changing settings, you should have at least one reliable speed test tool and a recent backup of your site. Then you can tweak one area at a time and retest. This method helps you see which optimizations matter and prevents guesswork.
What Slows Down a WordPress Site?
Most slow WordPress sites share a few common problems. Heavy themes, oversized images, and too many plugins add extra code to every page. Weak or overloaded hosting makes server responses slow. Third-party scripts, such as analytics or chat widgets, can also block rendering if they load in the wrong order.
Why Does Speed Matter for SEO?
Search engines favor pages that load fast and stay responsive as users scroll and click. Faster pages reduce bounce rates and help visitors view more content, which sends positive engagement signals. Better Core Web Vitals scores also support stronger search visibility on both mobile and desktop.
How to Measure Site Performance
You cannot improve WordPress speed optimization if you do not measure performance first, so testing comes before everything else. A good speed test shows how long your page takes to load, how quickly it becomes interactive, and which resources cause delays. With clear metrics, you can focus your effort on changes that move the needle.
How Do You Test WordPress Speed?
A practical approach is to test key pages, such as your homepage and top landing pages, with tools like PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or WebPageTest. Run several tests at different times of day to smooth out temporary network or server issues. Then take note of your average load time and Core Web Vitals scores.
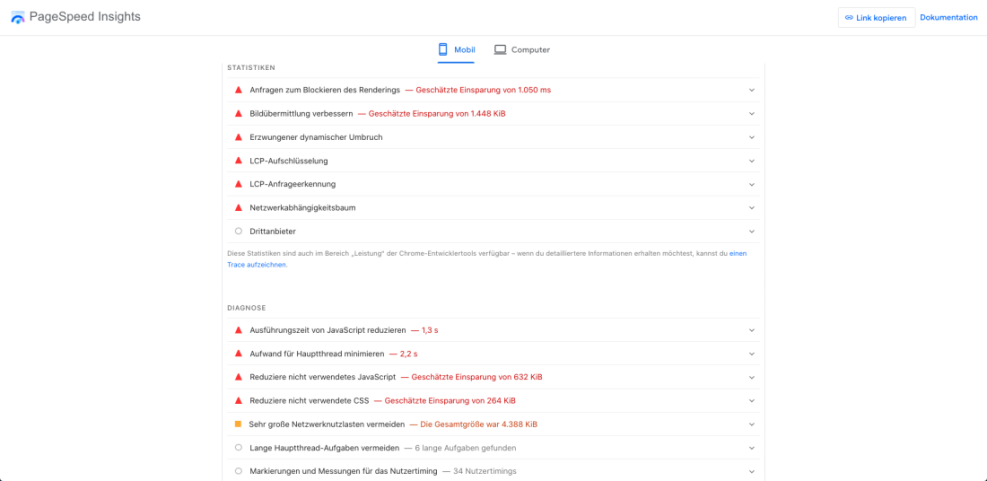
Which Metrics Should You Watch?
For most sites, focus on metrics like Time to First Byte, Largest Contentful Paint, Interaction to Next Paint, and Cumulative Layout Shift. These numbers show how fast your main content appears, how responsive your page feels, and how stable your layout remains as assets load. Lower times and smaller shifts almost always mean a better experience.
How Often Should You Benchmark?
Regular testing helps you catch regressions before visitors notice them. It makes sense to benchmark before and after major theme changes, plugin installs, or content overhauls. In addition, schedule monthly or quarterly checks so slowdowns from plugin updates or traffic growth do not go unnoticed.
Choose Hosting and Caching Wisely
Your hosting environment sets the ceiling for WordPress speed optimization. Even the best caching plugin cannot fully fix an overloaded or outdated server. When you choose a host that understands WordPress and provides modern infrastructure, every other optimization becomes more effective.
How to Choose Faster Hosting
Look for hosting that offers recent PHP versions, solid-state drives, and data centers near your main audience. Managed WordPress hosting often includes server-level caching, automatic updates, and security features that reduce extra plugin overhead. If you struggle with frequent timeouts, upgrading your plan usually brings a noticeable speed boost.
What Is WordPress Caching?
Caching stores a ready-made version of your pages, so the server does not rebuild them for every visit. Page caching helps anonymous visitors see content much faster. Object caching and opcode caching further speed up database queries and PHP execution, which is especially valuable on dynamic or high-traffic sites.
Which Caching Plugin Settings Matter Most?
Most caching plugins include many options, but a few matter the most. Start with page caching, browser caching, and basic HTML, CSS, and JavaScript minification. Then safely enable features like lazy loading for images. Always test the site after changing settings, because aggressive options can break forms, carts, or membership areas.
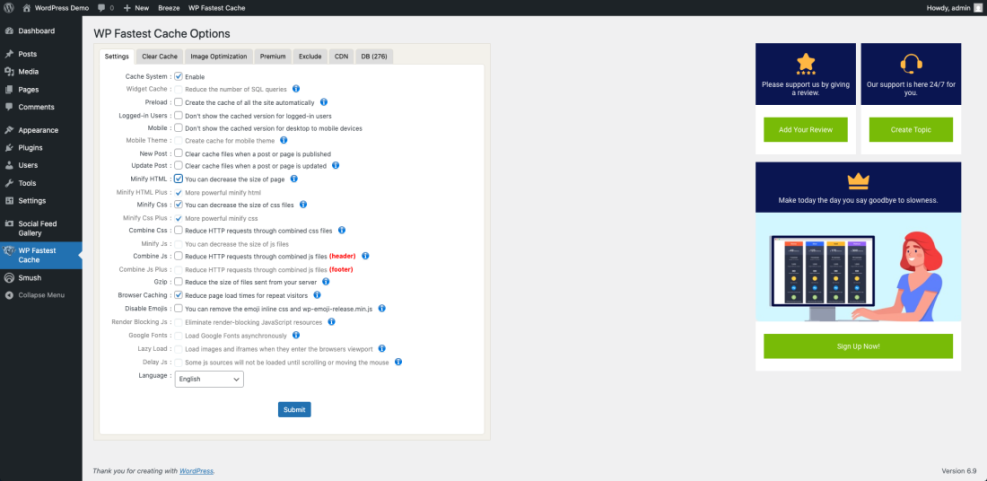
Optimize Images, CSS, and JavaScript
Media and front-end code often represent the largest portion of your page weight, so they are central to WordPress speed optimization. When you shrink images, remove unused CSS and JavaScript, and control when assets load, browsers can render your layout much faster. Visitors then see useful content without long blank or jittery screens.
Best Practices for Image Optimization
First, resize images to match their display size instead of uploading massive originals. Next, compress them with a plugin that supports modern formats like WebP. In addition, enable lazy loading so below-the-fold images load only when needed. These changes usually produce one of the biggest speed improvements on image-heavy pages.
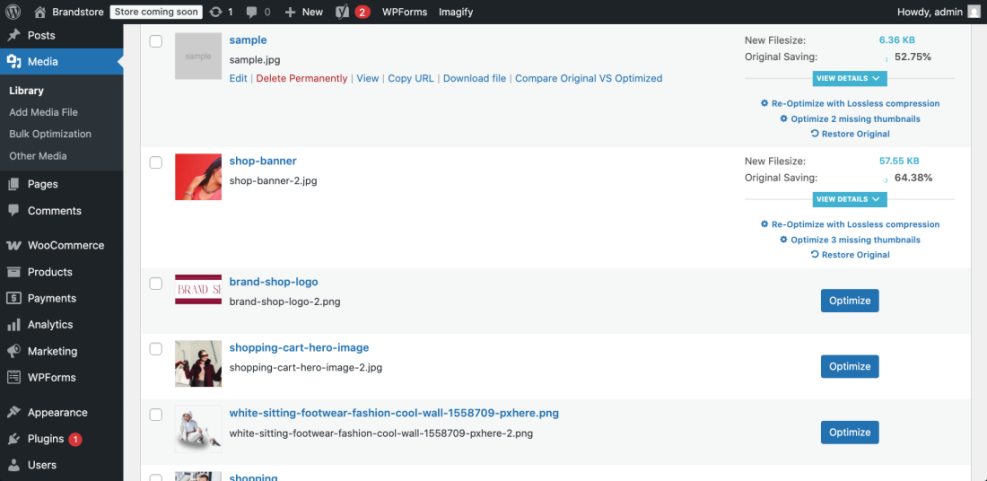
Should You Use a CDN for Assets?<
A content delivery network stores copies of your static files on servers across the world. Visitors receive assets from the closest location, which reduces latency and improves load times. A CDN becomes especially helpful when you serve global traffic, large images, or many script and style files.
- Serve compressed and resized images.
- Enable lazy loading for images and iframes.
- Combine or minify CSS and JavaScript where safe.
- Host static assets on a reliable CDN.
This simple checklist covers the core asset optimizations for most WordPress sites. When you implement these items and retest, you typically see smaller page sizes and faster rendering across devices.
How to Minify CSS and JavaScript<
Minification removes whitespace and comments from your styles and scripts to reduce file size. Many caching or performance plugins handle this with a few checkboxes. However, some complex themes or plugins may break when files merge, so start with minification only, then carefully test combined files and exclude any that misbehave.
Streamline Database, Plugins, and Themes
Behind the scenes, your database, plugins, and theme drive how many queries WordPress runs and how much code it loads. A lean setup reduces processing time on every request. Over months or years, clutter tends to build up, so periodic cleanup makes a real difference.
Clean Up the WordPress Database Safely
Database cleanup tools can remove old post revisions, trashed content, expired transients, and spam comments. Before you run them, create a full backup through your host or a backup plugin. Then clear one type of data at a time and retest your site to confirm everything works as expected.
How Many Plugins Are Too Many?
There is no strict number, but every plugin adds code and potential queries. You should periodically audit your plugins and remove those that duplicate features, have not been updated in a long time, or add heavy scripts on every page. This pruning often removes hidden performance drains and lowers the risk of conflicts.
If you run a complex store or membership site, consider consolidating features into fewer, well-supported plugins. For example, you might replace several small add-ons with a single robust suite that handles caching, security, and image optimization together.
Choose a Lightweight Theme for Performance
A lightweight, well-coded theme loads fewer assets and keeps your layout stable as content appears. Avoid themes that bundle many sliders, page builders, or visual effects you do not use. If you rely on WooCommerce or other complex plugins, look for themes built and tested specifically for those integrations.
For more in-depth guidance, you can plan a dedicated guide on Woocommerce optimization once your store grows. When you combine a lean theme with clean plugins, the rest of your WordPress performance work becomes much easier.
Focus on Core Web Vitals Metrics
Core Web Vitals translate technical performance into user-centered metrics. They track how quickly meaningful content appears, how soon people can interact, and how stable the layout stays. Strong scores show that your WordPress speed optimization work actually improves the real-world experience and supports long-term WordPress speed optimization goals.
What Are the Key Core Web Vitals?
The three main metrics to watch are Largest Contentful Paint, Interaction to Next Paint, and Cumulative Layout Shift. LCP measures how fast the largest element, such as a hero image or heading, appears. INP reflects how responsive the page feels when users tap or click. CLS tracks whether layout jumps as fonts, ads, or images load.
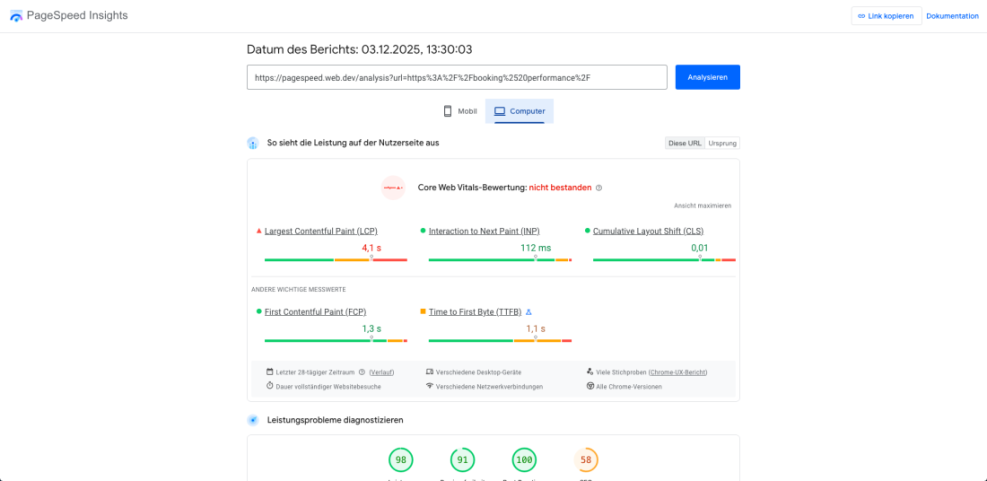
How Do You Improve LCP on WordPress?
To improve LCP, make sure your hero images are compressed and served in modern formats, reduce render-blocking CSS and JavaScript, and enable server and page caching. Hosting your fonts and critical assets on a CDN also helps. When the browser has fewer large files to fetch, it can show the main content much sooner.
How Can You Reduce Layout Shift?
To reduce CLS, always set width and height attributes for images and iframes so the browser reserves space. Avoid injecting banners or ads above existing content, and keep sticky headers to a predictable size. When elements do not suddenly appear or resize, visitors can read and click without losing their place.
For deeper technical background, you can review web performance documentation on sites like Google web.dev and the MDN performance module, then map their recommendations to your WordPress stack.
Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Performance is not a one-time project. As you publish new content, install plugins, and receive more traffic, your site’s behavior changes. Regular monitoring ensures small regressions do not turn into major speed problems that hurt your visitors and your revenue.
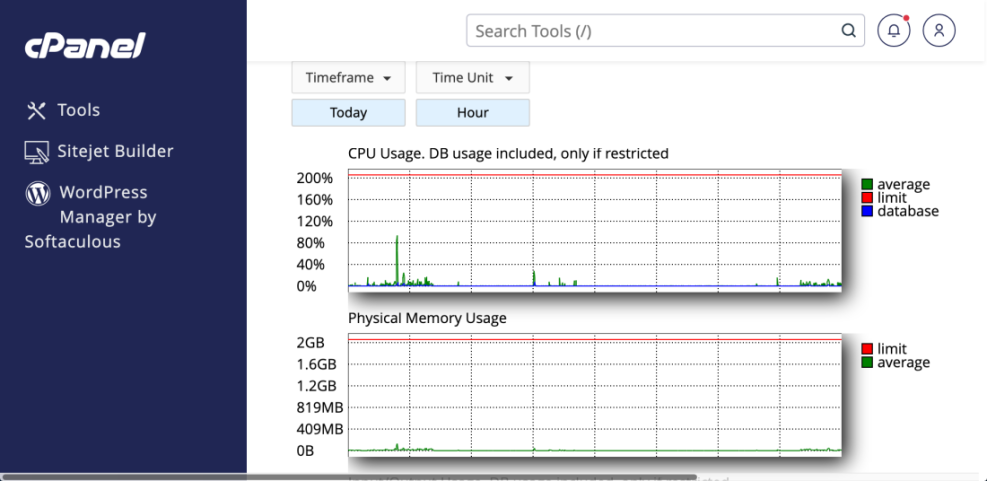
Set Up Ongoing Monitoring Tools
You can combine free and paid tools to watch your site. For example, scheduled runs in WebPageTest or similar services track how load times evolve. Server-level monitoring from your host reveals CPU, memory, and database load. When any graph trends upward, it may be time to scale resources or optimize heavy pages.
What Maintenance Tasks Should You Schedule?
Create a simple checklist you follow every month or quarter. Update WordPress core, themes, and plugins, then remove anything unused. Regenerate critical CSS if your performance plugin supports it, and reoptimize new images. This routine keeps your environment clean and reduces the chance of sudden slowdowns.
When Should You Call a Performance Expert?
Sometimes you hit a wall even after following best practices. If your site remains slow despite good hosting, caching, and lean assets, consider hiring a specialist. They can profile your code, analyze slow queries, and recommend deeper architectural changes that go beyond a typical plugin-based setup.
When you reach that point, detailed documentation from sources such as the WordPress.org performance handbook and Google PageSpeed tools provides a shared language for working with experts.
WordPress Speed Optimization Conclusion
At this stage, you have a clear WordPress speed optimization roadmap for making your site feel fast and reliable. You can measure performance with trusted tools, fix obvious bottlenecks in hosting and caching, and trim images, scripts, and database clutter that quietly slow everything down.
The next step is to pick one key page and apply these improvements in a controlled way. Run a baseline speed test, make a small set of changes, then retest. When your results improve, roll those same patterns across your site. Over time, you build a performance-first mindset into every design, content, and plugin decision.
If you are starting from scratch, consider following a clean installation path with a lightweight theme and a focused plugin set. You can then add features gradually and run fresh tests after each change. This approach creates a fast, resilient WordPress site that grows with your business instead of slowing it down.
More WordPress Guides You Might Like
Once you stabilize your site’s performance, you can explore related topics that build on the same foundation. The following planned guides deepen your knowledge and help you apply similar techniques in more specialized areas.
- WordPress seo complete beginners guide
- Woocommerce performance tips for faster stores
- Beginner guide WordPress speed core web vitals
- Woocommerce performance tips for faster stores
As these guides go live, you can combine them with this speed optimization framework to build a stable, secure, and fast WordPress platform that supports long-term growth.





