
If you are wondering what the Latest Version of WordPress is and whether you should update, you are not alone. WordPress releases new versions regularly to fix bugs, patch security issues, and add new features.
This guide will show you how to check which version of WordPress you are running, compare it against the newest release, and update safely without breaking your site.
What You Need Before Updating to the Latest Version of WordPress
- Administrator access to your WordPress dashboard.
- Access to your hosting control panel or FTP (for manual updates).
- A basic understanding of plugins and themes installed on your site.
- Enough disk space on your hosting to store a backup and run the update.
- A recent full backup of your files and database, or a backup plugin ready to run.
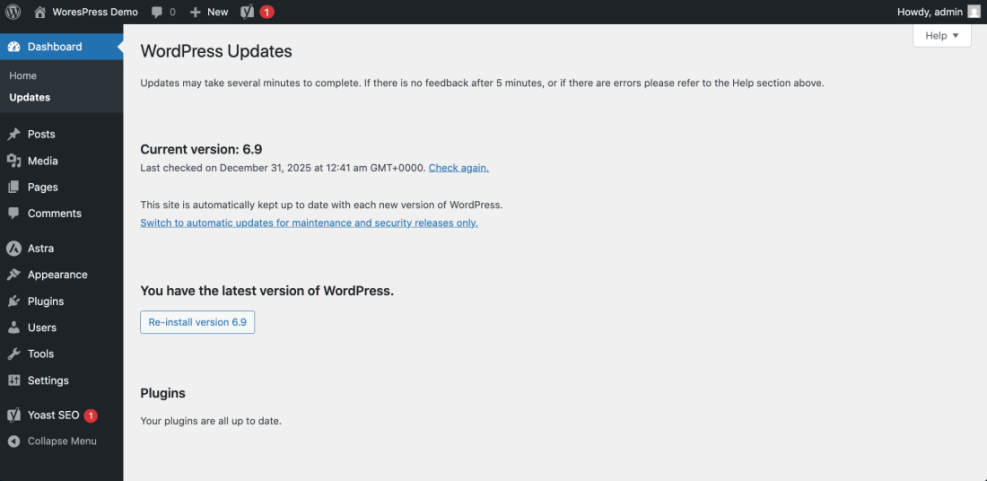
Step 1: Check Which Version Your Site Is Using
Before you compare with the latest WordPress release, you need to know what version your site is currently running.
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard (usually at
yourdomain.com/wp-admin/). - Look at the bottom right corner of the dashboard screen; many installations show the version number there.
- Alternatively, go to Dashboard » Updates. At the top of this screen you’ll see a message like “You have the latest version of WordPress” or “An updated version of WordPress is available.”
- Your current version number will also appear in this message or just below it.
Step 2: Find the Official Release Number
To know whether you are up to date, you must compare your site’s version with the official current WordPress version.
- Visit the official WordPress website in a new browser tab.
- On the download or homepage, look for the current release number (for example, 6.x.x).
- Compare that number to the version you saw in Dashboard » Updates.
- If your version is lower, it means a newer release is available and you should plan an update soon.
Step 3: Why Staying Updated Matters
Updating to the most recent WordPress core version is not just about getting new features. It’s primarily about security and stability.
- Security patches: New versions fix known vulnerabilities that hackers might exploit.
- Bug fixes: Updates resolve issues that can cause errors, warnings, or strange behavior.
- New features: You get improvements to the block editor, performance boosts, and design tools.
- Compatibility: Many themes and plugins are written for the newest WordPress version; staying up to date reduces conflicts.
Knowing this makes it easier to justify scheduling updates as part of your regular maintenance routine.
Step 4: Back Up Your Site Before You Update
Even though the update process is usually smooth, a backup is your safety net if something goes wrong.
- Install a trusted backup plugin if you do not already use one, or use your hosting provider’s backup tools.
- Create a full backup that includes:
- All WordPress files (themes, plugins, uploads).
- The WordPress database (posts, pages, settings).
- Download a copy of the backup to your computer or cloud storage if possible.
- Confirm that you know how to restore from the backup if necessary (check your plugin or host docs).
Step 5: Update to the Latest WordPress Version from the Dashboard
The easiest way to install the newest WordPress release is through the built-in updater in your dashboard.
- In your dashboard, go to Dashboard » Updates.
- If a new version is available, you will see a button labeled Update Now.
- Click Update Now. WordPress will put your site into maintenance mode while it downloads and installs the updated files.
- Wait until the process completes; do not close the browser tab during the update.
- When it’s finished, you’ll see a success screen with details of the version you just installed.
Step 6: Alternative Update Methods
For advanced users or special cases, there are additional ways to update WordPress to the current build.
- Hosting auto-installer: Some hosts offer a “One-click WordPress updater” in their control panel.
- Manual update via FTP:
- Download the latest WordPress package from the official site.
- Extract the files on your computer.
- Upload the
wp-adminandwp-includesfolders and core files (but notwp-content) over your existing installation. - Visit your site and follow any database update prompts.
- WP-CLI (command line): On supported hosting, you can run a command like
wp core updateto install the newest core version.
Quick Comparison of Ways to Get the Latest Version of WordPress
Use this table to choose the best update method for your skill level and hosting setup.
| Method | Where You Use It | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Dashboard “Update Now” Button | WordPress dashboard » Dashboard » Updates | Fast, one-click way for most site owners to install the latest WordPress version. |
| Hosting Auto-Updater | Hosting control panel » WordPress Manager / Apps | Let your host manage core updates automatically on a schedule or with a single click. |
| Manual FTP Update | FTP/SFTP client + file manager | Advanced method used when the automatic update fails or you need more control. |
| WP-CLI Command Line | SSH terminal with WP-CLI installed | Developers can script or automate updates for multiple WordPress sites. |
| Staging Site First | Staging subdomain or copy of site | Test a new WordPress release safely before updating your live site. |
Step 7: Troubleshoot Problems After an Update
Sometimes installing a new WordPress core version reveals plugin or theme conflicts. Here’s how to handle common issues.
- White screen or fatal error: Disable plugins via FTP by renaming the
wp-content/pluginsfolder, then reactivate them one by one. - Theme layout broken: Switch temporarily to a default theme to see if the issue is theme-related.
- Update stuck in maintenance mode: Delete any
.maintenancefile in your site’s root via FTP. - Site extremely slow: Clear caches (plugin + server + browser) and regenerate critical CSS if your theme supports it.
- Still broken: Restore from your backup and investigate on a staging copy of the site.
Conclusion: Staying on the Latest Version of WordPress Keeps Your Site Safe
Now you know how to find the Latest Version of WordPress, check which version your site is running, and update safely using the dashboard, your host, or manual tools.
Make updating a regular habit: back up first, check for new releases, and test key pages after each update. Staying on a recent WordPress version helps protect your site, keeps features fresh, and ensures your themes and plugins work as intended.





