
If you are asking whether WordPress is hard to learn, you are not alone. Many beginners look at the dashboard, settings, and plugins and worry that WordPress will be too technical or confusing.
The good news is that basic WordPress tasks are beginner friendly when you follow a clear path. In this guide, you will understand the real WordPress learning curve, see which parts feel hard and why, and follow a simple plan to gain confidence without feeling overwhelmed.
What You Need to Start Learning WordPress
- Comfort using a web browser, copying and pasting text, and saving files on your computer.
- A WordPress site you can safely practice on, such as a new installation, a demo site from your host, or a local installation on your own computer.
- Login details for the WordPress admin area, usually the Username and Password created during installation.
- At least 60–90 minutes of focused time without interruptions for your first practice session.
- A willingness to click, test, and undo changes rather than expecting everything to be perfect on the first try.
Is WordPress Hard to Learn? Understanding the Learning Curve
The biggest reason WordPress feels hard is not that the software is complicated, but that it can do so many different things. A simple blog uses only a small part of what WordPress can do, while an online store, membership site, or custom application uses much more.
Think of your learning in three levels:
- Beginner user — You can log in, create posts and pages, add images, and manage basic settings.
- Confident site owner — You can choose and customize a theme, install plugins safely, manage menus, and handle basic speed and security tasks.
- Developer level — You can write custom code, build themes and plugins, and debug complex issues.
Most small business owners and bloggers only need to reach the first or second level. You can safely ignore developer skills until you truly need them.
Set Up a Safe Practice Site to Learn WordPress
WordPress feels much easier when you know you can experiment without breaking anything important. A separate practice site lets you click freely and learn faster.
- Ask your host if they offer a staging site or one-click WordPress install. Use that instead of your live site when possible.
- Next, open your browser and go to your WordPress admin URL, usually https://yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
- On the login screen, enter your Username and Password, then click Log In.
- After logging in, check the site name in the top-left corner of the Dashboard to confirm this is your test site.
- If you are completely new to WordPress, read What is managed WordPress to understand how the dashboard, themes, and plugins fit together.
You will know this step is successful when you can log into the dashboard and feel comfortable practicing without worrying about breaking your real site.
Core Skills That Make Learning WordPress Easier
Instead of trying to learn everything, focus on a small set of core tasks. Once you can do these without thinking, WordPress will stop feeling scary.
Create a blog post:
-
- From the left menu, click Posts » Add New.
- Then type a title in the top field, add a paragraph block, and write a short post.
- When you are happy with the content, click Publish, then choose View Post to see it on your site.
Create a basic page:
-
- Open the Pages menu in the sidebar and select Add New.
- Now create a simple About page with a heading and a short paragraph.
- Finally, click Publish, then preview the page on the front end.
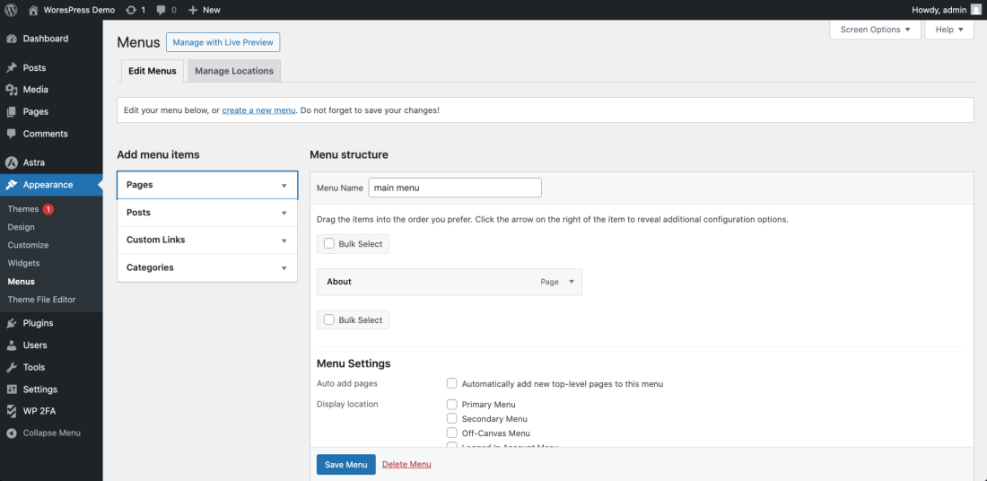
Adjust your site navigation:
-
- Go to Appearance » Menus (or Appearance » Editor for block themes).
- Use the menu interface to add your new About page to the main menu and rearrange the order if needed.
- After updating, save the menu and refresh your site to confirm the new link appears.
Change your theme safely:
-
- Start by opening Appearance » Themes.
- From there, click Add New Theme, preview a design, and then click Activate only on your practice site.
- After activation, review your homepage and a blog post to see how the layout changes.
Install a trusted plugin:
-
- Head to Plugins » Add New from the admin menu.
- Search for a popular plugin such as a contact form or SEO tool with many active installs and good reviews.
- Once you have chosen a plugin, click Install Now, then Activate, and look for its settings under Settings or its own menu.
Once you can repeat these tasks without checking notes, everyday WordPress use will feel much easier.
How Long Does It Take to Learn WordPress?
How hard WordPress feels depends heavily on how far you want to go and how much time you can invest each week. You do not need years of study to manage a simple site.
- First wins in a day — With a guided checklist like How to start a blog WordPress, you can have a basic site online in a single day.
- Comfortable daily use in a few weeks — Spending an hour a day for two to four weeks is enough for most people to become confident site owners.
- Developer level in months or longer — Learning PHP, JavaScript, and theme or plugin development is a separate path that takes months or more of focused study.
For most small sites, you never need to become a developer. You only need to reach the level where you can publish, update, and maintain your site without stress.
Why WordPress Seems Hard to Learn (and What’s Actually Difficult)
It is helpful to separate the easy, medium, and hard parts of WordPress so you can focus on what matters now and ignore the rest.
- Usually easy — Writing posts, creating pages, managing menus, and uploading images.
- Moderate — Choosing a theme, configuring plugins, setting up contact forms, and handling performance or basic SEO.
- Advanced — Custom code in themes or plugins, complex WooCommerce setups, custom post types, and API integrations.
If you ever decide to go deeper, guides like How to build a website on WordPress and Is WordPress good for seo will help you move into the next level one step at a time.
Ongoing WordPress Maintenance While You Learn the Platform
As you become more comfortable with WordPress, you will also need to learn how to keep your site updated, backed up, and secure. Different methods offer different levels of control and complexity. This table gives you a quick overview:
| Method | Where You Use It | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Manual Maintenance | WordPress dashboard and hosting control panel | Maximum control over updates, backups, and checks for small or low-risk sites. |
| Managed Hosting Tools | Your host’s control panel or custom dashboard | Simplify routine maintenance with one-click updates, built-in backups, and basic security. |
| Maintenance & Security Plugins | Plugins section inside the WordPress dashboard | Automate repetitive work like backups, database cleanup, image optimization, and security scans. |
| WP-CLI and Developer Tools | SSH terminal with WP-CLI and deployment tools | Scriptable, fast maintenance for developers managing multiple or complex sites. |
| Professional WordPress Care Plan | External provider, freelancer, or agency | Hands-off maintenance with proactive monitoring, fixes, and expert support. |
Notice how the methods at the top of the table are easier to start with and use mostly the dashboard, while the bottom rows involve more advanced tools or hiring professionals. You can begin with the simple options and move up only if and when you need them.
7-Day Plan to Learn WordPress Without Feeling Overwhelmed
Instead of trying to learn everything at once, use a short study plan. That approach keeps WordPress from feeling hard and gives you small wins every day.
- Day 1 — Read How to start a blog WordPress and log into your practice site.
- Day 2 — Create your first post and page using the block editor.
- Day 3 — Adjust your main menu and practice changing themes.
- Day 4 — Install a contact form plugin and create a simple contact page.
- Day 5 — Explore basic settings under Settings » General and Settings » Reading.
- Day 6 — Review beginner security tips from this security basics checklist for new store owners even if you do not run a store yet.
- Day 7 — Read How to use ai in WordPress and check which tasks already feel easy.
What Advanced WordPress Code Looks Like When You Keep Learning
You do not need to write code to use WordPress as a beginner. However, seeing a small, real example can help you understand what “advanced” really means.
The following snippet registers a custom menu location in a theme. You would only touch code like this if you decide to learn theme development later.
function mytheme_register_menus() {
register_nav_menus(
array(
'primary' => __( 'Primary Menu', 'mytheme' ),
)
);
}
add_action( 'after_setup_theme', 'mytheme_register_menus' );
Conclusion: So, Is WordPress Hard to Learn?
WordPress is not hard to learn when you focus on real tasks instead of trying to understand everything at once. Basic skills like creating posts, pages, menus, and installing a few trusted plugins are very achievable for non technical users.
To make progress, use a safe practice site, follow a simple weekly plan, and repeat the same core actions until they feel natural. When you are ready to do more, you can go deeper into design, performance, or even development at your own pace. For now, you have everything you need to begin.
Further Reading to Help You Learn WordPress
- Beginner guide to WordPress speed optimization
- How to install a WordPress theme
- Beginner checklist optimizing WordPress blog posts
- Is WordPress good for seo
- WordPress migration checklist for blogs





