
WordPress SEO is one of the main reasons so many site owners choose the platform, and the short answer is yes, WordPress can be very good for SEO when you configure it correctly. Out of the box, it gives you a flexible content management system that can be tuned for fast, crawlable, and well structured pages that search engines understand.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to decide whether WordPress is the right SEO foundation for your site, how to configure core settings, which plugins and performance tweaks matter, and how to structure your content so your WordPress site can earn and keep strong rankings over time.
What You Need Before You Start
- An existing self hosted WordPress site with access to /wp-admin.
- An administrator account so you can change Settings and install Plugins.
- Basic familiarity with editing posts or pages in the Classic Editor or your preferred editor.
- A recent backup of your site or a staging environment before you change performance or SEO settings.
Step 1: Understand WordPress SEO Strengths and Limits
Why WordPress Is a Strong Platform for SEO
Before you change anything, you need to understand what WordPress does well for SEO and where it needs help. This makes it clear that WordPress is a strong SEO foundation, but not a magic ranking button.
Check Your Current WordPress SEO Setup
- Log in to your dashboard at https://yourdomain.com/wp-admin using an administrator account.
- Navigate to Dashboard » Updates and confirm that your WordPress core is up to date.
- Go to Appearance » Themes and note which theme you are using, for example Jannah.
- Navigate to Plugins » Installed Plugins and look for any SEO plugin such as Yoast, Rank Math, All in One SEO, or SEOPress.
Navigate to Dashboard » Plugins to quickly scan which SEO and performance tools are already active on your site.
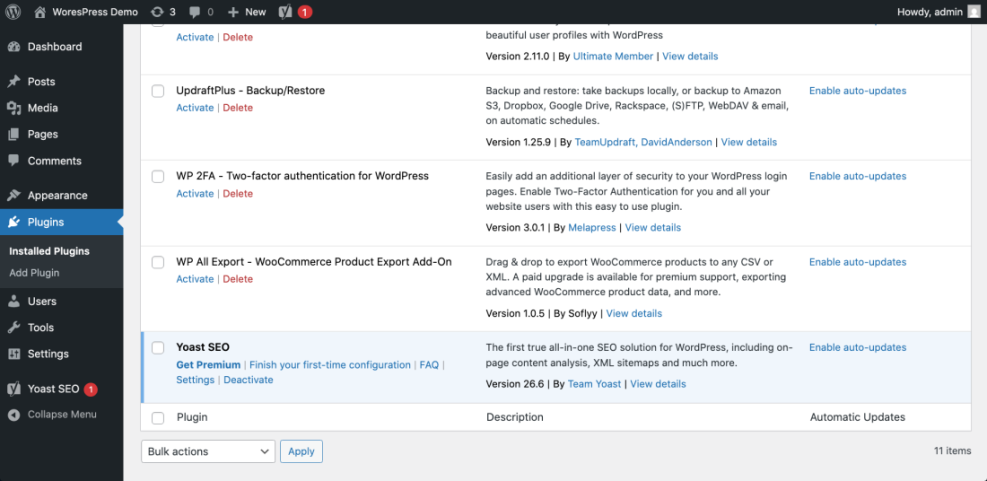
Confirm You Have the Right Ingredients
If you can confirm that your site runs a modern WordPress version, a responsive theme like Jannah, and at most one SEO plugin, you already have the basic ingredients for a good SEO setup. WordPress is a solid SEO platform, but you must configure and maintain it to get results.
For a deeper conceptual overview, you can also read What is seo on WordPress in a separate tab once you finish this tutorial.
Step 2: Configure Core Site Settings
WordPress can only be good for SEO if your core settings make sense for search engines. Here you will ensure that search engines are allowed to crawl, your URLs are clean, and key site identity fields are meaningful.
Allow Search Engines to Index Your WordPress Site
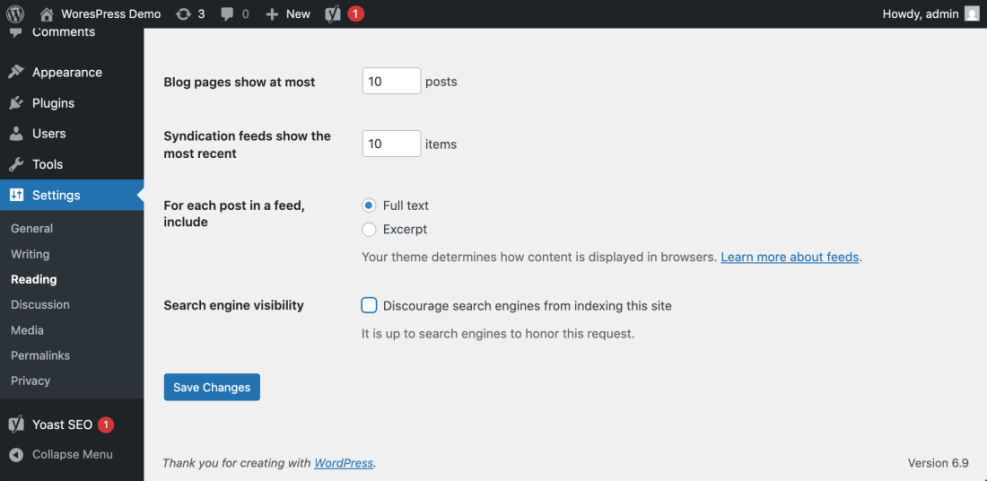
- Navigate to Settings » Reading.
- Find the option Search engine visibility and make sure the checkbox Discourage search engines from indexing this site is unchecked.
- Scroll down and click Save Changes if you modified anything.
On the same screen, verify that Search engine visibility allows indexing before continuing.
Set SEO Friendly WordPress Permalinks
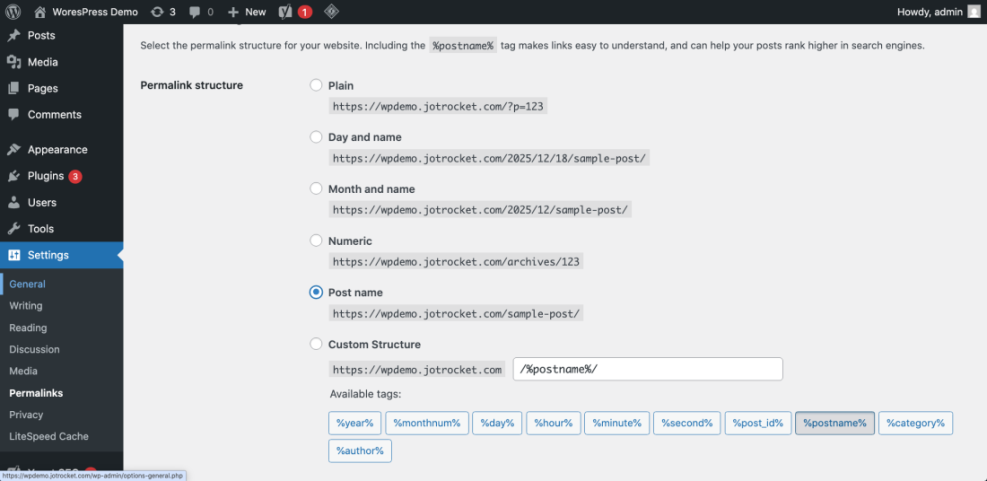
- Go to Settings » Permalinks.
- Select the Post name option, which creates SEO friendly URLs based on your post titles.
- Click Save Changes.
Navigate to Settings » Permalinks to confirm that Post name is selected and your URL examples look clean and keyword rich.
Improve Your Site Title and Tagline
- Go to Settings » General.
- Set Site Title to a clear brand plus key topic, not just “My Blog”.
- Change Tagline from the default “Just another WordPress site” to a short description of what your site offers.
- Click Save Changes.
After these changes, visit one of your posts in a new browser tab and look at the address bar and browser tab title. The URL should be human readable and the title should reflect your brand and topic clearly, which is exactly what search engines prefer.
If you want more guidance on structuring categories and tags, open Categories tags beginner guide in a new tab to review once you finish this tutorial.
[Optional] Noindex Low Value Search Pages
If you are comfortable adding small snippets via a child theme or the Code Snippets plugin, you can also prevent low value search pages from being indexed by adding this optional code:
/**
* Add noindex to WordPress search results pages.
* Place in a child theme's functions.php or a code snippets plugin.
*/
function wph_noindex_search_results() {
if ( is_search() ) {
echo '<meta name="robots" content="noindex,follow" />' . "n";
}
}
add_action( 'wp_head', 'wph_noindex_search_results' );After adding this snippet, perform a search on your site and view the page source to confirm the <meta name="robots" content="noindex,follow"> tag is present.
Step 3: Install and Configure a WordPress SEO Plugin
WordPress core does not include full control over titles, meta descriptions, XML sitemaps, or breadcrumb markup by itself. An SEO plugin fills these gaps so WordPress can compete with any modern CMS from an SEO perspective.
Choose and Install a Single WordPress SEO Plugin
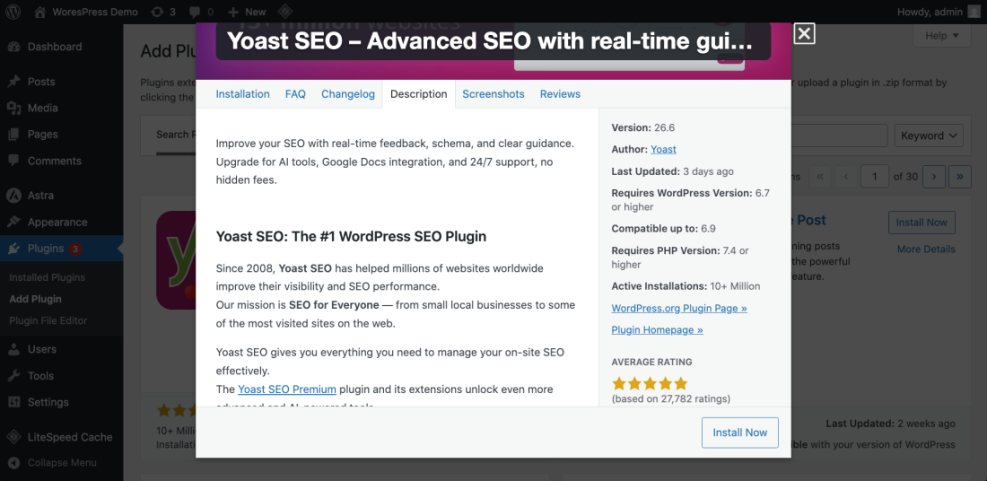
- In your dashboard, go to Plugins » Add New.
- In the search box, type SEO and review trusted options such as Yoast SEO, All in One SEO, Rank Math, or SEOPress.
- Click Install Now on your chosen plugin, then click Activate.
On the Plugins » Add New screen, search for “SEO” and hover over your chosen plugin to see its rating, active installs, and last updated date.
Run the Setup Wizard
- After activation, look for the new SEO menu in your dashboard, such as SEO or Rank Math.
- Launch the plugin’s setup wizard and follow the prompts to set your site type, company or person name, social profiles, and basic technical settings.
- Enable automatic XML sitemaps if the plugin offers them, and keep default settings for advanced options unless you are sure you need to change them.
Open one of your posts in the editor and scroll to the SEO meta box added by your plugin. You should now see fields for SEO title, meta description, and focus keyword. This confirms that your SEO plugin is working and giving WordPress the extra controls it needs.
For a safer configuration walkthrough, plan to follow Yoast seo setup guide once you have finished this overview.
Step 4: Improve WordPress Performance and Speed
Search engines reward sites that load quickly and provide a smooth user experience. WordPress can be very good for SEO here because you control hosting, caching, images, and theme performance instead of being locked into a slow platform.
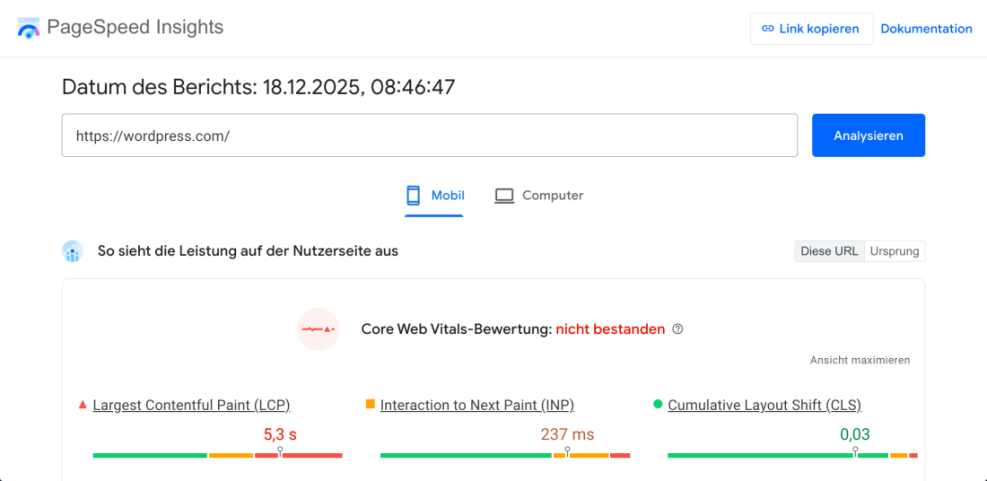
Measure Your Baseline WordPress SEO Performance
- Open a new tab and visit PageSpeed Insights (pagespeed.web.dev).
- Enter your homepage URL and click Analyze.
- Review your mobile and desktop scores and note the Core Web Vitals suggestions.
Use PageSpeed Insights to see how your current WordPress setup performs before you change anything.
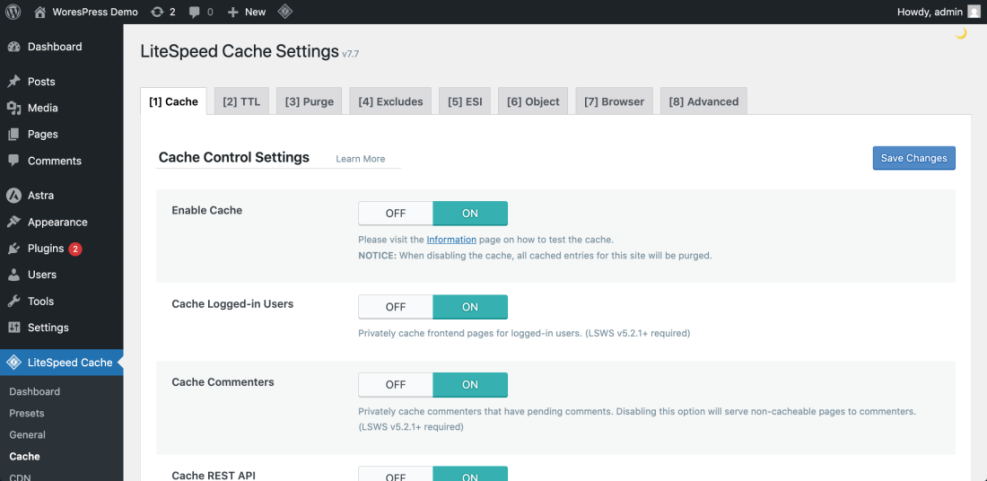
Enable Caching on Your WordPress Site
- Return to your dashboard and go to Plugins » Add New.
- Search for a reputable caching plugin compatible with your host.
- Click Install Now, then Activate.
- Follow the plugin’s quick setup wizard to enable page caching and, if offered, browser caching.
Navigate to the caching plugin’s settings page from the new menu item (for example Settings » Caching) to verify that caching is enabled and the plugin reports “Cache status: On”.
Optimize Images and Retest Performance
- Install an image optimization plugin or manually compress large images before upload.
- Retest your homepage in PageSpeed Insights and compare the scores and Core Web Vitals against your baseline.
If you see improved performance scores and faster load times after enabling caching and optimizing images, you have made WordPress significantly better for SEO, especially on mobile.
Step 5: Create SEO Friendly Content Structure in WordPress
Even with perfect settings and plugins, WordPress is only good for SEO if your content is structured clearly and internally linked. This step focuses on how you use the editor, headings, and links to help search engines understand your pages.
Use Headings and Keywords for Better WordPress SEO
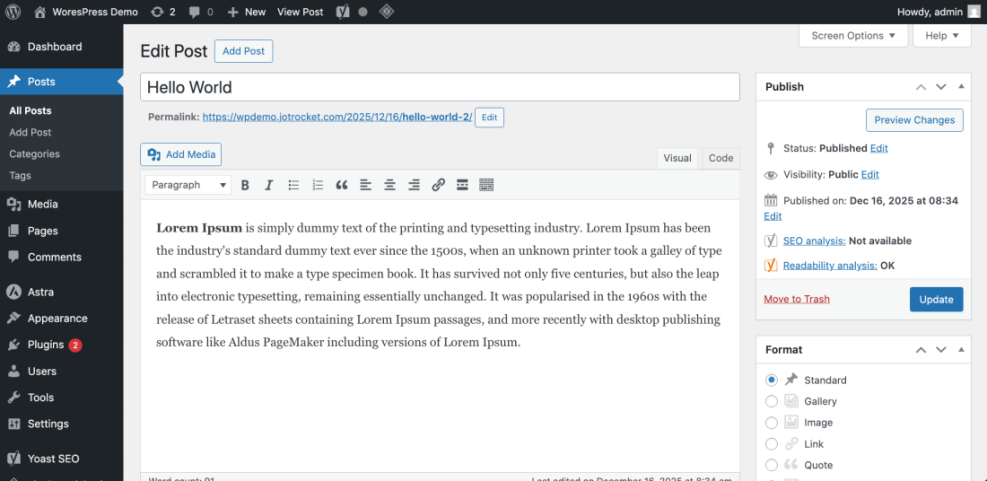
- From your dashboard, go to Posts » All Posts.
- Hover over one of your most important blog posts and click Edit.
- In the editor, confirm that your main title is in the H1 field and your subtopics use H2 and H3 headings logically.
- Scan the content for your target keyword phrase and make sure it appears naturally in the title, first paragraph, and at least one subheading.
While editing the post, scroll through the content and ensure each section has a clear heading rather than long unstructured blocks of text.
Strengthen Internal Links and URLs
- Select a relevant phrase in the content, click the Insert/edit link icon, and link to another helpful post on your site.
- Add links to key hub pages and recent posts where it helps readers, not just for search engines.
- Check the Slug field (or permalink) near the title and simplify it to use a few descriptive words if needed.
- Click Update to save your changes.
After updating, view the post on the front end and confirm that headings are easy to scan, links help readers discover related content, and the URL is short and descriptive. This is exactly the type of structure search engines reward.
When you are ready to go deeper into categorization and hubs, read Best WordPress seo plugins and tools to design topic clusters around your main keywords.
Step 6: Track Your WordPress SEO Performance Over Time
One of the biggest advantages of WordPress for SEO is how easily it integrates with analytics and search data tools. Tracking your results shows whether your WordPress SEO work is actually paying off.
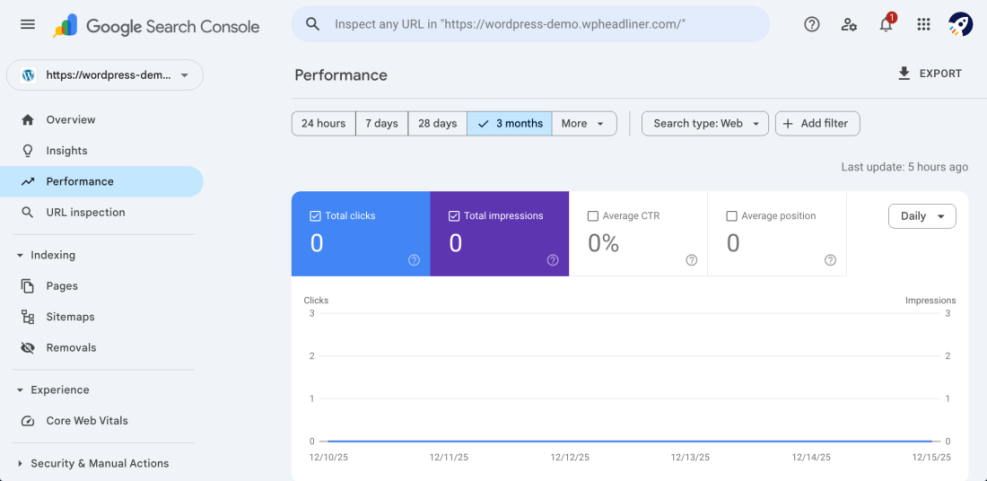
Connect Google Search Console for WordPress SEO Insights
- Sign in to your Google account and open Google Search Console in a new tab.
- Click Add property and choose the Domain or URL prefix option that matches your site.
- Follow the on screen instructions to verify your site, using DNS or HTML tag verification, depending on what you are comfortable with.
Once verified, click on your property in Search Console and open the Performance report to see queries, clicks, and impressions.
Add Analytics Tracking to Your Site
- Set up analytics tracking on your site using your preferred method (plugin or manual code).
- In WordPress, install an analytics plugin if needed and paste in your tracking ID following the plugin’s instructions.
- Wait at least 24 hours, then confirm page views are appearing in your analytics reports.
Common Ways to Handle WordPress SEO Maintenance
As you start monitoring rankings and traffic, it helps to choose a maintenance approach that keeps your WordPress site healthy, secure, and fast. Here are the most common methods site owners use:
| Method | Where You Use It | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| DIY Manual Maintenance | WordPress dashboard and hosting control panel | Maximum control over updates, backups, and checks for small or low-risk sites. |
| Managed Hosting Tools | Your host’s control panel or custom dashboard | Simplify routine maintenance with one-click updates, built-in backups, and basic security. |
| Maintenance & Security Plugins | Plugins section inside the WordPress dashboard | Automate repetitive work like backups, database cleanup, image optimization, and security scans. |
| WP-CLI and Developer Tools | SSH terminal with WP-CLI and deployment tools | Scriptable, fast maintenance for developers managing multiple or complex sites. |
| Professional WordPress Care Plan | External provider, freelancer, or agency | Hands-off maintenance with proactive monitoring, fixes, and expert support. |
Choose the option that matches your budget, time, and technical comfort. Consistent maintenance means fewer technical SEO issues, smoother updates, and more reliable performance over the long term.
After a few weeks of consistent content and optimization work, review both Search Console and analytics. You should begin to see increasing impressions, clicks, and organic sessions if your WordPress SEO configuration and content are working together.
To systematize this tracking inside WordPress, plan to review Analytics setup WordPress google analytics once you have the basics in place.
Conclusion: Your Site Is Ready to Grow
So, is WordPress good for SEO The answer is yes, when you treat it as a flexible platform that you configure and maintain, not as a set and forget site builder. With the right core settings, a single well configured SEO plugin, fast performance, and clear content structure, WordPress can match or outperform most other platforms for organic search.
You have now checked your WordPress foundations, improved your URLs and site visibility, installed SEO and caching plugins, tuned content structure, and connected analytics. Keep publishing high quality content and iterating on performance, and your WordPress site can become a long term SEO asset.
Further Reading
- Complete beginner’s guide to SEO on WordPress
- SEO roadmap for new WordPress blogs: from zero to first rankings
- How to add keywords in WordPress without hurting
- Internal linking WordPress beginners
- Beginner guide to WordPress speed optimization





