How to Fix Broken Links in WordPress
Find and repair 404 errors without hurting site performance

Broken Links in WordPress quietly damage your SEO, frustrate visitors with 404 errors, and waste valuable crawl budget. The good news is that you can systematically find and fix them using a mix of plugins, Google Search Console, and smart redirects.
In this step by step guide, you will scan your site for broken links, fix them directly inside the WordPress editor, add 301 redirects for removed content, and set up a simple maintenance routine so broken links never pile up again.
What You Need to Start
- Administrator access to your WordPress dashboard.
- A recent full site backup or snapshot (see your Beginner guide to WordPress speed optimization if you need help).
- Optional but recommended access to Google Search Console for your domain.
- Basic understanding that a 404 error means “page not found” and a 301 redirect means “moved permanently”.
Step 1: Set up a broken link scanner
First, you need a reliable way to discover where broken links live on your site. A dedicated broken link checker plugin can scan internal and external URLs without overloading your server.
- Log in to your WordPress admin dashboard.
- Go to Plugins » Add New.
- In the search box, type Broken Link Checker.
- Locate a trusted plugin such as Broken Link Checker by AIOSEO and click Install Now, then Activate.
- After activation, look for the plugin menu (for example Link Checker or All in One SEO » Broken Links).
- Start a scan or ensure automatic scanning is enabled so the plugin crawls your posts, pages, and other content.
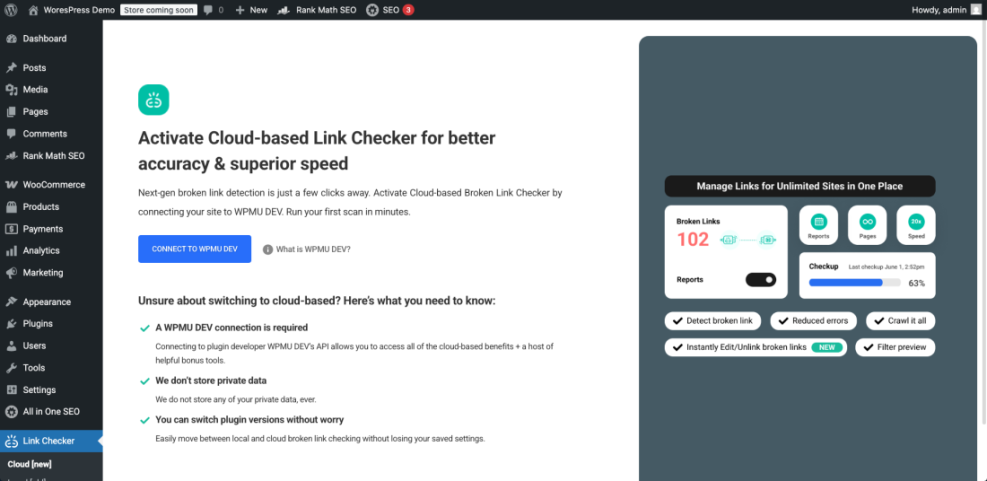
Wait for the scan to finish. You should see a list of URLs with a status like 404 or Timeout, plus the posts or pages where each broken link appears. Once you see that report, your scanner is working correctly.
Step 2: Find broken links with Google Search Console
Plugins work inside WordPress, but Google Search Console shows which URLs Google itself is hitting and seeing as errors. This helps you prioritize the broken links that matter most for search.
- Open Google Search Console in your browser and select your property.
- In the left sidebar, click Indexing then Pages (or Pages under the appropriate section in the new interface).
- Filter for issues such as Not found (404) or similar error types.
- Click any error type, then scroll down to the list of affected URLs.
- Select one URL and use the Inspect URL or View crawled page option to confirm it is truly broken.
- Copy each important broken URL into a working list you will fix in WordPress.
To verify success later, you will come back to this report. Once you have fixed links and created redirects, Google should gradually remove those 404 URLs from the error list after it recrawls your site.
Step 3: Fix broken links in WordPress content
With your list of problem URLs ready, the next step is to update or remove the individual links inside your posts, pages, menus, and widgets. This fixes the broken paths visitors actually click.
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Posts » All Posts or Pages » All Pages.
- Use the search box to find the post or page listed in your broken link report.
- Click the title to open it in the editor (Classic Editor or block editor).
- Highlight the anchor text of the broken link, then click the link icon (Insert/edit link).
- Update the URL field with the correct working URL, or delete it to unlink if the destination is no longer needed.
- Click Apply or press Enter, then click Update to save the post or page.
If the broken link points to another page on your own site, consider whether the anchor text and surrounding copy are still accurate. Use this as a chance to strengthen your internal linking strategy. For a deeper walkthrough, review the Internal linking WordPress beginners.
To verify each fix, open the updated post in a new browser tab and click the link yourself. It should load the correct page without errors or endless redirects.
Step 4: Redirect deleted or moved URLs
Sometimes the content a link points to is gone or has moved to a new URL. In those cases, the best solution is a 301 redirect so both users and search engines are sent to the new, most relevant page.
- From your WordPress dashboard, go to Plugins » Add New and search for a redirect manager plugin (for example Redirection or your SEO plugin’s redirect module).
- Click Install Now, then Activate.
- Open the plugin screen such as Tools » Redirection or SEO » Redirects.
- In the Source URL or From field, paste the old broken URL (for example
/old-page/). - In the Target URL or To field, paste the new, relevant URL (for example
/new-page/). - Set the redirect type to 301 Moved Permanently and click Add Redirect or Save.
If you manage redirects at the server level, you can also add a simple rule in your .htaccess file on Apache based hosting:
Redirect 301 /old-page/ https://example.com/new-page/For a wider view of your technical health, combine these fixes with your Is WordPress good for seo so every crawl issue, not only broken links, is addressed.
To verify redirects, open a private browser window and visit the old URL. It should jump instantly to the new destination and show a 200 OK status when checked with your browser’s network tools.
Step 5: Schedule regular broken link checks
Broken links will slowly appear again as you publish new content, change URLs, or link to external sites that later disappear. A simple maintenance routine keeps everything under control.
- Open your broken link checker plugin settings under Settings or its own menu.
- Set a sensible scan frequency such as weekly or monthly, and enable Email notifications for new issues.
- Add a repeating calendar reminder titled “Broken link review” so you regularly log in to handle the plugin’s report.
- Once a month, review the Not found (404) section in Google Search Console to catch any URLs your plugin missed.
- For larger sites, periodically crawl your domain with a desktop crawler like Screaming Frog SEO Spider or a cloud based SEO audit tool to cross check results.
As you repeat this process, your broken link reports will get shorter and easier to manage. Most monthly reviews should only take a few minutes once the initial cleanup is done.
Conclusion You Are Ready to Go
You have now scanned your WordPress site for Broken Links, fixed them directly in your posts and pages, and created 301 redirects for URLs that had to change. You have also set up a recurring maintenance routine so new broken links are caught early.
With cleaner internal and external links, visitors hit fewer dead ends, search engines crawl your content more efficiently, and your overall technical SEO improves. Keep refining your process as your site grows, and broken links will stay a minor maintenance task instead of a major emergency.
Further Reading
- Is WordPress good for seo
- Internal linking strategies WordPress
- WordPress seo complete beginners guide





