WordPress Backup Strategy That Never Fails
A Practical Plan To Keep Your Website Safe

A solid WordPress backup strategy is the only thing standing between a small mistake and a complete site disaster. When something breaks, you either click Restore and move on, or scramble for hours trying to rebuild everything.
With a clear plan, you can automate backups, store them safely, and practice restores so you are confident that nothing is ever truly lost. This guide walks you through building a layered backup plan, choosing tools, setting a realistic schedule, and avoiding the mistakes that cause backups to fail when you need them most.
WordPress Backup Strategy Essentials
The quickest way to build a WordPress backup strategy that never fails is to combine three layers: your hosting backups, a dedicated backup plugin, and offsite cloud storage. Then you schedule automatic backups, keep 3–5 recent copies, and regularly test a restore on a staging site.
For most sites, a strong baseline is daily database backups, weekly full site backups, at least one copy stored outside your hosting account, and a monthly test restore. This approach protects you from hacks, broken updates, human errors, and hosting failures while keeping recovery fast and predictable.
What Does a Reliable Backup Plan Include?
A reliable plan covers your entire site, not just the database. It includes scheduled full backups, extra backups before big changes, offsite storage, and a simple restore process that you have already tested. It also defines who is responsible for checking logs and verifying that new backups are actually created.
How Many Backups Should You Keep?
As a rule of thumb, keep at least three to five recent backups, with copies stored in different locations. One can live with your host, one in a cloud storage account, and one on your own computer or company drive. This way, if any single backup fails, you still have another clean copy to restore.
How Often Should You Back Up WordPress?
Backup frequency depends on how often your content or orders change. Busy blogs and online stores usually need at least daily backups, while quieter brochure sites may get by with weekly ones. However, if you cannot afford to lose a day of data, you should run database backups more often than that.
Design Your Backup Layers
A backup strategy that never fails does not rely on one tool. Instead, you build layers so that if one system breaks, another can still save you. Think of it as a safety net made of several strong ropes rather than a single thread.
Use Your Hosting Backups Wisely
Most quality WordPress hosts offer automatic backups, often kept for several days or weeks. You should check how often they run, how long they keep copies, and how easy it is to restore a single site. However, you should never rely only on hosting backups, because they live on the same infrastructure you are trying to protect.
Add a Dedicated Backup Plugin
A backup plugin gives you control from inside the WordPress Dashboard. Good plugins can back up your database and files, schedule different frequencies, and send backups to remote storage services such as Google Drive, Dropbox, Amazon S3, or SFTP. This keeps your backups close to your workflow and easy to restore.
From the WordPress Dashboard, go to Plugins » Add New and search for your preferred backup plugin, then open its settings page once it is active.
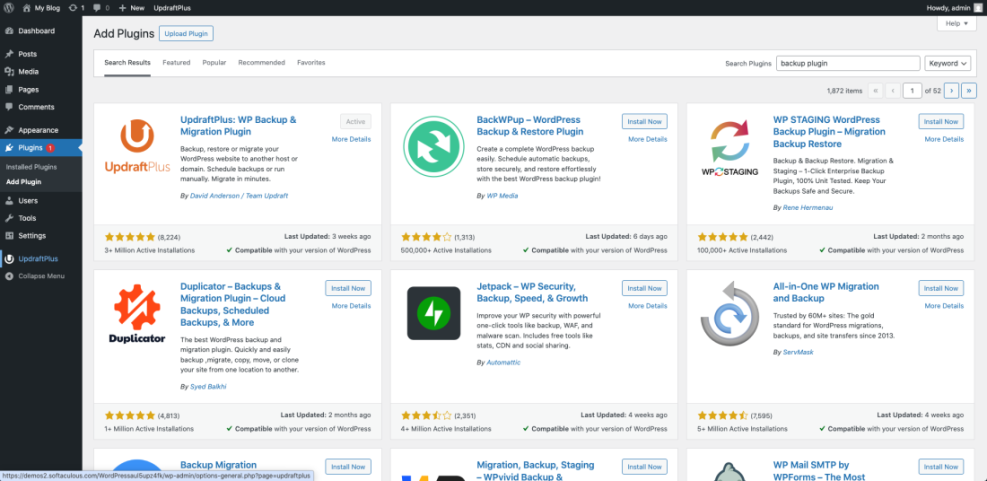
Many site owners use plugins like UpdraftPlus, BackWPup, Jetpack Backup, or BlogVault for this layer. Whichever tool you choose, make sure it can store backups away from your server and that it supports simple, one-click restores.
Why Offsite Cloud Storage Matters
Offsite storage protects you from server failures, data center issues, or even simple mistakes like deleting the wrong folder. When your backups live in a different place, your site and your backups are unlikely to fail at the same time. Popular choices include Google Drive, Dropbox, Amazon S3, or a secure company cloud drive.
Choose Backup Methods And Tools
Once you know your layers, you can pick the actual methods that fit your skills and budget. You can mix manual backups, plugins, and hosting tools so you always have at least one backup method you fully understand.
Manual Backups With cPanel And phpMyAdmin
Manual backups take more time, but they give you full control and are useful before risky changes. You back up the database and the files separately, then store the archives somewhere safe.
- Log in to your hosting control panel and open phpMyAdmin.
- Select your WordPress database, click the Export tab, and download an SQL file.
- Open the File Manager, compress the public_html or site folder, and download the ZIP file.
- Store both files in a labeled folder on your computer or company drive.
In your hosting control panel, open phpMyAdmin from the Databases section before starting the export.
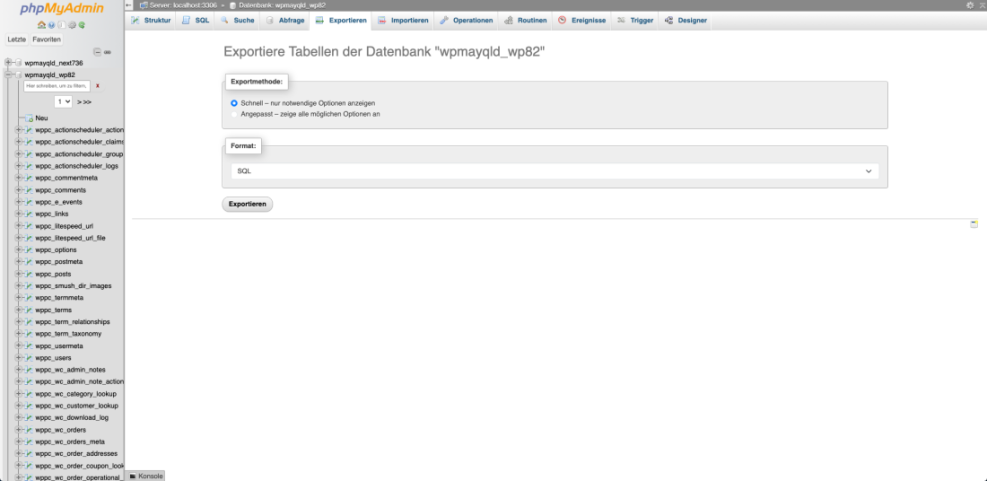
Manual backups are a good fallback method for emergencies and can also help you understand how your site is structured behind the scenes.
Recommended WordPress Backup Plugins
A backup plugin automates most of the work for you. The best options support scheduled backups, incremental backups that only store changes, and direct connections to cloud storage. They also make restores simple, often with a single button and a progress log.
Look for a plugin that can back up both the database and the wp-content folder, supports your favorite storage service, and has clear restore steps. Before committing, try a test restore on a staging site or local copy.
For more technical details about backup best practices, the official WordPress.org backup handbook is a helpful reference.
Advanced Option Command Line Backups
If you are comfortable with SSH and WP-CLI, you can run backups from the command line and schedule them with cron. This method avoids plugin overhead and works even if WordPress is not loading correctly, as long as the server is running.
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +%F-%H%M)
cd /var/www/html
# Export database
wp db export ~/backups/wp-db-$DATE.sql
# Archive wp-content
tar -czf ~/backups/wp-files-$DATE.tar.gz wp-content
# Remove backups older than 30 days
find ~/backups -type f -mtime +30 -delete
When you compare methods, it helps to visualize the trade-offs in a simple table.
| Method | Main Pros | Main Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hosting Backups | Automatic, managed by host, easy full restore | Tied to same server, limited control, short retention |
| Backup Plugin | Flexible schedules, offsite storage, simple restores | Uses site resources, depends on WordPress loading |
| Manual or WP-CLI | Full control, works even when plugins fail | Requires technical skills, easy to forget steps |
This overview makes it easier to build a mix that suits your site and your comfort level with technical tools.
Set Up And Test Your Schedule
A backup that never runs is as bad as no backup at all. After you choose tools, you need a simple schedule that you actually follow and that reflects how often your site changes.
Create a Simple Backup Schedule
You can start with a schedule that matches your content flow, then adjust later if needed. The goal is to limit your maximum possible data loss to a level you can accept.
- List how often you publish posts, get new comments, or receive orders.
- Set database backups at least as often as that activity, usually daily.
- Set full file backups weekly or twice per week for busy sites.
- Plan extra backups before major plugin, theme, or core updates.
- Review the schedule every few months and adjust if your site grows.
If you want a deeper checklist that includes updates and monitoring, consider creating a custom WordPress maintenance schedule that you can review alongside your backup plan.
Configure Schedules In Your Plugin
Backup plugins usually let you pick schedules and storage in a few clicks. Although each plugin looks different, the process follows the same basic pattern.
- Open the backup plugin settings in the WordPress Dashboard.
- Choose a database backup frequency, such as every 12 or 24 hours.
- Choose a file backup frequency, such as weekly.
- Select a remote storage option and connect your account.
- Set how many backups to retain before old ones are deleted.
- Save your settings and run the first manual backup.
In the WordPress Dashboard, go to Settings » Your Backup Plugin and open the scheduling tab to confirm that everything is enabled.
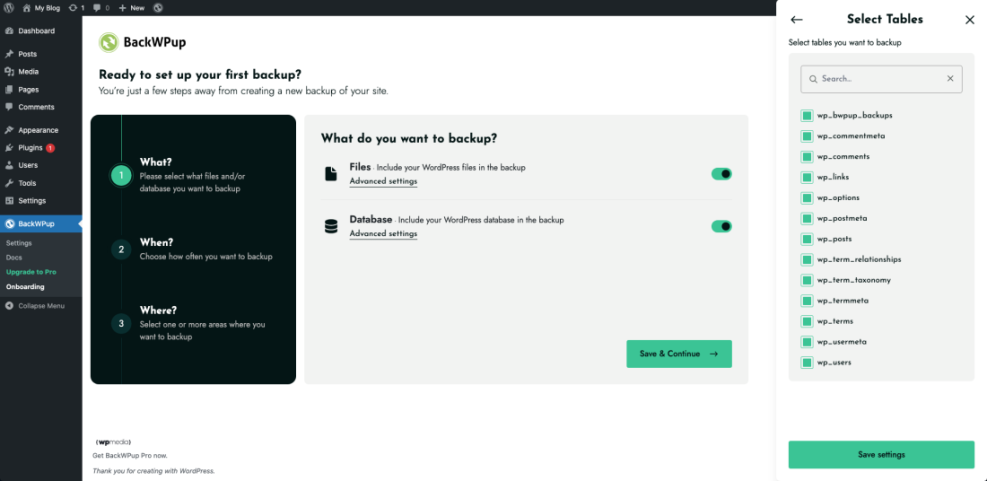
After the first backup completes, check the logs and make sure the file appears in your chosen cloud storage account.
Test a Restore on a Staging Site
A backup is not trustworthy until you have restored it at least once. Testing on a staging site or temporary clone allows you to practice the steps and confirm that everything works.
- Ask your host to create a staging copy or use a plugin that can clone your site.
- Restore a recent backup to the staging site using the same tool you would use in production.
- Browse the staging site, log in, and verify that pages, forms, and checkout still work.
- Document the restore steps so you or a teammate can follow them under pressure.
In your hosting dashboard, open the Staging or Clone tool and select your main site before starting the restore test.
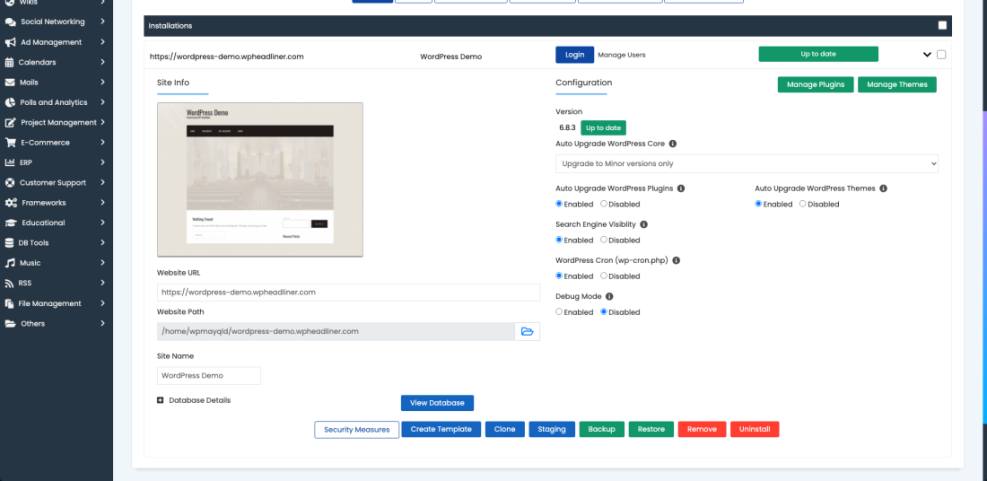
Once you confirm that restores work as expected, you gain real confidence that your WordPress backup strategy will protect you during a crisis.
Protect And Monitor Your Backups
Backups themselves become valuable targets, because they contain full copies of your site and database. You need to secure them and keep an eye on their health just like you monitor your live site.
Secure Backup Files And Access
You should treat backup files as sensitive data. Store them in locations that require strong authentication, such as cloud buckets with user access controls, not in publicly accessible folders on your server. When possible, enable encryption at rest and in transit, and limit who can download or restore backups.
Avoid These Common Backup Mistakes
Several recurring problems cause backups to fail when you most need them. You can avoid a lot of pain by checking for these issues now rather than later.
- Storing backups inside the public web root where visitors can access them.
- Keeping only a single backup copy or letting all copies live on one server.
- Letting backup storage fill up until new backups silently fail.
- Running heavy backups during peak traffic hours, slowing the site down.
- Never testing a restore, so broken backups stay unnoticed for months.
When you fix these weak spots early, your backups become more reliable, and you reduce the risk that a small oversight turns into a major outage.
Can You Delete Old Backups Safely?
You can safely delete older backups as long as you keep a healthy rotation of recent ones. A simple approach is to keep a few daily copies, a few weekly copies, and one or two older monthly backups. As long as you retain several clean restore points, pruning very old archives frees up space without adding much risk.
WordPress Backup Strategy Conclusion
A WordPress backup strategy that never fails is not about one perfect plugin. It is about stacking simple habits and tools so that any single problem still leaves you with a fast way back online. When you combine hosting backups, a dedicated backup plugin, and offsite storage, you gain real resilience.
- Automatic backups for database and files.
- At least one offsite copy in the cloud.
- Clear retention rules and monitoring.
- Documented, tested restore steps.
Your next step is straightforward: choose one backup plugin, connect a cloud storage account, set a realistic schedule, and run your first test restore on a staging site. Once that process feels routine, you will know your backups are ready for anything.
More WordPress Backup Strategy Guides You Might Like
To round out your protection and maintenance workflow, it helps to explore a few related topics in more detail. These resources fit naturally with the backup plan you just created.
- How to create a website with WordPress
- WordPress migration checklist for blogs
- How to use ai in WordPress
- How to publish WordPress site
- Common WordPress Backup Errors And How To Fix Them
You can treat these topics as the next building blocks in your long-term security and maintenance plan, turning one strong backup strategy into a complete safety net for your site.





