
Edit robots.txt in WordPress to control what search engines can crawl and index on your site. With a well configured robots.txt file, you prevent bots from wasting crawl budget on low value areas without accidentally blocking important content.
In this step by step guide you will learn how to find your current robots.txt file, edit it safely using plugins or file manager, create an advanced robots.txt with code if needed, and test everything so your SEO stays healthy.
What You Need to Start
- Admin access to your WordPress dashboard.
- Access to your hosting control panel or FTP, if you plan to edit files directly.
- A recent backup of your site or at least of the public_html (or site root) folder.
- Basic understanding that robots.txt controls how search engines crawl your site.
Step 1: Understand robots.txt basics
Before you edit robots.txt in WordPress, understand what this file does. Robots.txt lives in your site root and tells search engine crawlers which paths they may or may not request.
- Know that the file must be available at https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt.
- Remember that most crawlers treat robots.txt as instructions, not hard security. It does not hide sensitive data.
- Understand that misusing Disallow can remove content from search results if crawlers cannot access it.
How to verify Read through a sample robots.txt and identify which folders are blocked and which are allowed, so the syntax feels familiar before touching your own file.
Step 2: Find your current robots.txt
Next, check whether a robots.txt file already exists for your WordPress site. WordPress can generate a virtual robots.txt, or you may have a physical file on the server.
- Open a browser and go to https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt (replace yourdomain.com with your real domain).
- Review the text shown. If you see rules like User-agent and Disallow, a robots.txt is active.
- If you see a 404 page, there is no robots.txt file, or something is blocking access.
How to verify Try the robots.txt URL in an incognito window and on mobile. You should see the same text without redirects or errors.
Step 3: Compare methods to edit robots.txt
There are several ways to edit robots.txt in WordPress. Use this quick comparison table to pick the method that matches your skills and hosting setup.
| Method | Where You Use It | Main Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SEO Plugin robots.txt Editor | WordPress Dashboard » SEO plugin » Tools / File editor | Edit robots.txt rules safely with a simple interface and basic validation. |
| Hosting File Manager / FTP | cPanel / Hosting panel » File Manager or FTP client | Directly create or edit the robots.txt file in your site root. |
| Code Snippets / Child Theme | functions.php or snippets plugin | Generate a dynamic robots.txt using the WordPress robots_txt filter. |
| Managed WordPress / WordPress.com Settings | Platform SEO or search settings panel | Apply limited robots.txt changes when direct file access is restricted. |
| Staging Site First, Then Live | Staging URL » then production site | Test new robots.txt rules safely before pushing them to your live site. |
In the next steps, you will see how to use the most common and practical options: SEO plugin editors, file manager / FTP, and code snippets.
Step 4: Edit robots.txt with an SEO plugin
The safest way to edit robots.txt in WordPress is through a reputable SEO plugin. This method avoids direct file edits and usually includes basic validation.
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard at https://yourdomain.com/wp-admin.
- Navigate to Plugins » Add New.
- Search for your preferred SEO plugin such as Yoast SEO or another trusted SEO plugin.
- Click Install Now and then Activate.
- In the left menu, go to the plugin menu such as SEO » Tools or SEO » File editor depending on the plugin.
- Open the robots.txt editor area provided by the plugin.
- Adjust the rules as needed, then click Save changes or Save robots.txt.
How to verify Visit https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt again in your browser. Confirm that the content matches what you just saved in the plugin.
Step 5: Edit robots.txt with file manager
If your SEO plugin does not offer a robots.txt editor or you prefer direct control, you can edit the file in your hosting control panel or via FTP.
- Log in to your hosting control panel and open File Manager, or connect via an FTP client.
- Navigate to your site root, usually public_html or a folder named for your domain.
- Look for an existing robots.txt file.
- If it exists, right click and choose Edit or View/Edit in your file manager or FTP client.
- If it does not exist, create a new file named robots.txt in the site root.
- Paste or adjust your robots.txt rules, then save the file.
How to verify Refresh https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt in a new browser tab. Confirm that the updated text appears without download prompts or formatting issues.
Step 6: Create robots.txt with code
Advanced users can generate robots.txt dynamically using WordPress filters. This avoids a physical file and keeps rules in version controlled PHP.
- Ensure you are using a child theme or a code snippets plugin so core theme files are not edited directly.
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Appearance » Theme File Editor, or open your child theme files via SFTP.
- Open functions.php in your child theme or create a new snippet in your code snippets plugin.
- Add a filter to robots_txt to define your custom rules.
- Save your changes and clear any server or plugin cache.
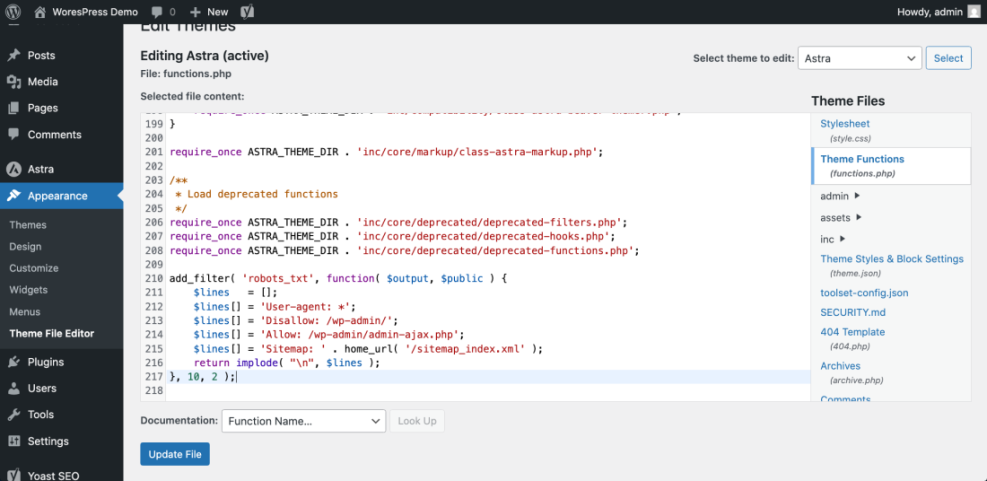
add_filter( 'robots_txt', function( $output, $public ) {
$lines = [];
$lines[] = 'User-agent: *';
$lines[] = 'Disallow: /wp-admin/';
$lines[] = 'Allow: /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php';
$lines[] = 'Sitemap: ' . home_url( '/sitemap_index.xml' );
return implode( "n", $lines );
}, 10, 2 );How to verify Visit https://yourdomain.com/robots.txt and confirm that it now shows the rules defined in your PHP filter. You can reference the official WordPress robots_txt hook documentation for more details on parameters.
Step 7: Test robots.txt and fix issues
After any change, you must test your robots.txt to ensure that important URLs remain crawlable and low value paths are blocked as intended.
- List a few important URLs such as your homepage, main category pages, and top posts.
- Confirm none of these URLs are disallowed by the paths you added to robots.txt.
- Check that admin areas like /wp-admin/ are disallowed but /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php remains allowed.
- Log in to your Google Search Console property and use URL Inspection to test a few key URLs for crawlability.
- Monitor crawl stats and indexing reports over the next few days for any sharp drops or errors.
How to verify Your key pages should remain indexed, while unnecessary system paths stay out of crawl reports. Watch for new index coverage errors related to blocked resources and adjust rules if necessary.
Conclusion You Are Ready to Go
You have learned several safe ways to edit robots.txt in WordPress, from SEO plugins to direct file edits and code based filters. You can now tune how search engines crawl your site without risking accidental deindexing.
Keep your robots.txt simple, review it regularly after theme or plugin changes, and always test important URLs after updates. With a clear and well maintained robots.txt, crawlers spend more time on the content that actually matters for your rankings.
Further Reading
- Is WordPress good for seo
- Is WordPress good for seo
- Yoast seo setup guide
- How to add keywords in WordPress without hurting
- How to add keywords in WordPress without hurting
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a robots.txt file for my WordPress site
Can I edit robots.txt on WordPress.com
What is a safe default robots.txt for WordPress
User agent all, disallow /wp-admin/, allow /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php, and add a Sitemap line pointing to your sitemap index. Avoid blocking public content, themes, uploads, or key plugin URLs.





