How to Do On Page SEO in WordPress
Optimize every WordPress post for higher rankings and more traffic

On page SEO in WordPress is the process of optimizing each post or page so that search engines and visitors understand your topic quickly and clearly. Rather than guessing what matters, you can follow a simple checklist every time you publish new content. This consistent workflow helps more of your posts rank, attract clicks, and turn visitors into subscribers or customers.
In this guide you will walk through the WordPress editor and your SEO plugin step by step. By the end, one post will be fully optimized from top to bottom, and you will have a repeatable process you can apply to every article or landing page you create.
What You Need to Start
- A WordPress site where you can log in as an Administrator or Editor.
- An SEO plugin installed and activated. If you do not have one yet, follow How to Install a WordPress SEO Plugin Step by Step.
- Basic keyword research completed for the topic you want to rank for.
- At least one draft or existing Post or Page ready to optimize.
- A recent backup of your site from your host or backup plugin.
Step 1: Choose Your Focus Keyword
Every on page SEO workflow starts with one clear focus keyword. This is the main phrase you want a specific post or page to rank for, plus a few closely related variations. A focused topic gives search engines a clear signal about what your content covers.
Find a realistic keyword
- Open your favorite keyword research tool in a new browser tab.
- Type in your topic idea and review phrases that match your content and audience.
- Select one main keyword with realistic search volume and difficulty for your site’s current authority.
- Write down two or three related phrases you can use in headings and body text.
- Keep this list open while editing so you can easily copy and paste phrases into your content where they fit naturally.
Once you have a primary keyword and a handful of related phrases that match search intent, you can move on to optimizing the actual post.
Step 2: Open Your Post Editor and SEO Panel
Now it is time to connect your chosen keyword to a real WordPress post so the SEO plugin can analyze it. The basic steps are similar whether you use the Classic Editor or the block editor.
Load the post you want to optimize
- Log in to your WordPress dashboard at /wp-admin.
- In the left menu, click Posts » All Posts (or Pages » All Pages).
- Hover over the post you want to optimize and click Edit.
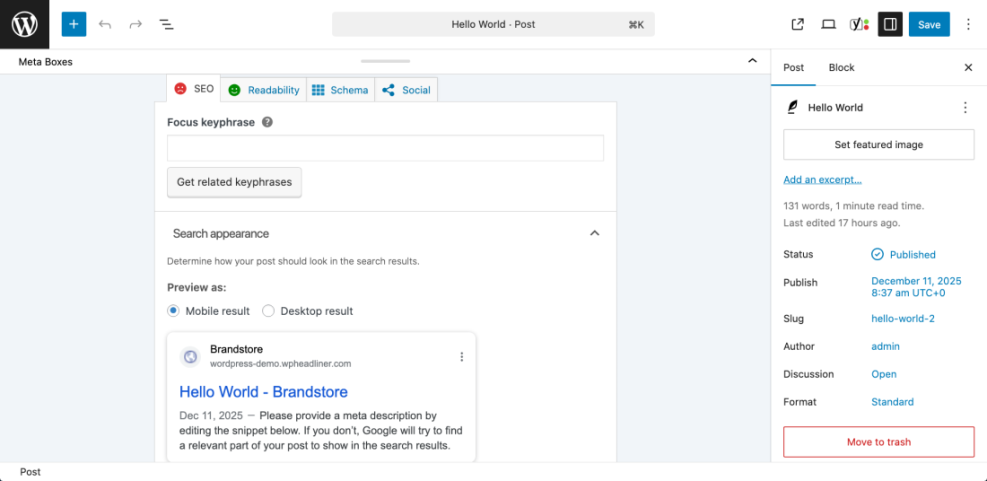
Set the focus keyphrase in your SEO plugin
- Scroll below the content editor until you see your SEO plugin panel, such as Yoast SEO, All in One SEO, or Rank Math.
- Find the field named Focus keyphrase or Focus Keyword.
- Enter your chosen focus keyword exactly once in that field.
- Click Save Draft or Update to store the change.
After saving, the SEO plugin will display an analysis checklist or score based on your focus keyword.
Step 3: Optimize Your URL Slug
The URL slug helps both Google and humans understand what a page is about. A short, descriptive slug that includes your main keyword is easy to read and more likely to earn clicks in search results.
Edit the slug in WordPress
- In the post editor, locate the Permalink or URL Slug setting.
- In the block editor, click the Post tab, then open the Permalink section.
- In the Classic Editor, look directly under the title for the Permalink field and click Edit.
- Change the slug to a short phrase that includes your main keyword, using only lowercase letters and hyphens. Example:
on-page-seo-wordpress. - Remove stop words like “and” or “the” and strip out unnecessary extra words.
- Click OK (if shown) and then click Update or Save Draft.
Check the preview above the editor and confirm the URL looks clean, readable, and obviously matches your topic.
Step 4: Create an SEO Title With Your Keyword
The SEO title is the blue, clickable headline that appears in search results. It should contain your focus keyword, promise a benefit, and stay within the recommended length so it displays neatly.
Write a search-friendly SEO title
- In the SEO plugin panel, locate the field labeled SEO Title or Title.
- Begin your title with, or very close to, your focus keyword. For example: “How to Do On Page SEO in WordPress”.
- Add a short benefit phrase such as “Step by Step Guide” or “for Higher Rankings”.
- Watch the plugin’s length meter and adjust until the preview suggests your title will not be truncated.
- Click Update or Save Draft.
Use the search snippet preview inside your SEO plugin to confirm the title fits on one line and looks compelling.
If your theme still uses hard coded <title> tags and does not support dynamic titles, you can add theme support in a child theme only.
function jannah_child_theme_setup() {
add_theme_support( 'title-tag' );
}
add_action( 'after_setup_theme', 'jannah_child_theme_setup' );
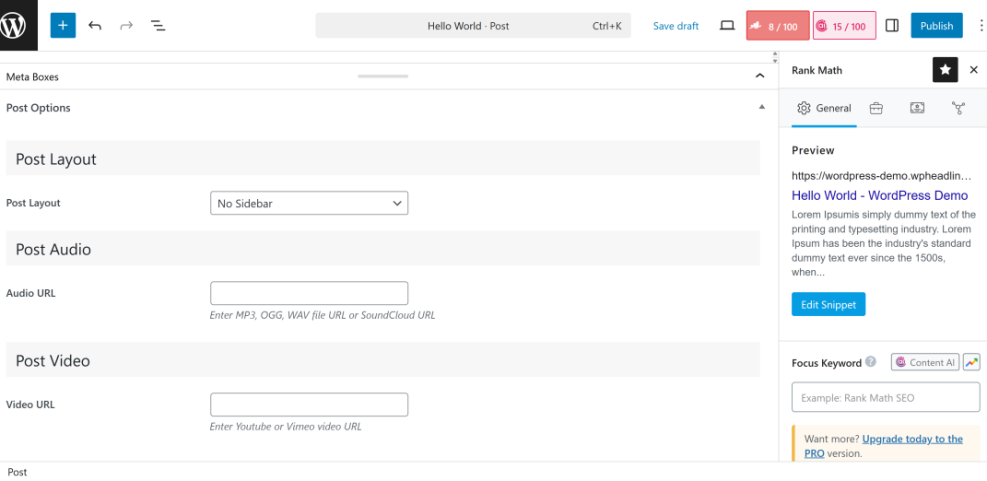
Step 5: Write a Compelling Meta Description
The meta description is the short summary shown under your SEO title in search results. Although it is not a direct ranking factor, a clear description with your keyword helps more people choose your result.
Craft a description that earns clicks
- In the SEO plugin panel, find the Meta description field.
- Write one or two natural sentences that describe the main value of your page.
- Include your focus keyword once, plus one related phrase if it fits smoothly.
- Keep the description around 150–160 characters, using the plugin’s length bar as a guide.
- Click Update or Save Draft.
Check the live preview in your SEO plugin and make sure the description is complete, inviting, and not cut off in the middle of a sentence.
A good meta description reads like a short ad for your content and contains the keyword without feeling stuffed or awkward.
Step 6: Structure Your Content for On Page SEO
Search engines and readers rely on your headings, paragraphs, and lists to understand how your content is organized. When the structure is logical and easy to scan, engagement improves and ranking potential increases.
Outline your main sections
- Review your post and note the main points you want to cover.
- Turn each main point into an H2 heading using the editor’s Paragraph / Heading dropdown.
- Use H3 headings for subsections under each H2 where you go into more detail.
Use headings and keywords wisely
- Include your focus keyword in one or two headings where it fits naturally.
- Place related phrases in other headings to support the topic without repeating the exact keyword everywhere.
Make paragraphs easy to scan
- Break long paragraphs into shorter blocks of two to four lines so the text is easier to read.
- Use bullet or numbered lists whenever you describe steps, tips, features, or examples.
Scroll through the post and confirm that each heading clearly describes the section beneath it and that no area feels like a wall of text.
If your SEO plugin includes a readability analysis, aim for a result that suggests the content is easy to read and well structured.
Step 7: Optimize Images, Internal Links and Publish
Images and internal links send strong on page SEO signals. Correct image alt text improves accessibility and topical relevance, while internal links help search engines understand how your content fits with the rest of your site.
Optimize your images
- Click on each image inside your post in turn.
- In the right sidebar, fill in the Alt Text field with a short, descriptive phrase that reflects the subject of the image. Add your focus keyword only when it truly matches what the image shows.
- Check that images are not oversized. Compressed formats and appropriate dimensions should be used before uploading.
Add internal and external links
- Highlight meaningful phrases in your content where an internal link would help readers get more information.
- Click the Link icon in the toolbar, type a keyword from another article, and select the relevant post from the suggestions to create an internal link.
- Add at least two or three internal links to closely related posts and, when appropriate, one high-quality external link such as official documentation or a trusted resource.
- Click Preview to confirm all images load quickly and every internal link points to the correct page.
Use this step to build a healthy internal linking structure that supports all of your on page SEO work. For more ideas, see Internal Linking Strategies for WordPress Content.
When images load fast, alt text is filled in, and your post points to other relevant pages, the article is ready to publish or update.
Conclusion You Are Ready to Go
By now you have walked through the complete workflow for on page SEO in WordPress. During the process, you chose a focus keyword, optimized the URL, title, and meta description, structured your content, and improved images and internal links.
The same steps can be applied to every new post or page you create. As you repeat this on page SEO process across your site, search engines will understand your topics more clearly, click-through rates can improve, and you are likely to see a steady increase in qualified organic traffic.





